Ranking of the best laser cutting machines for 2025
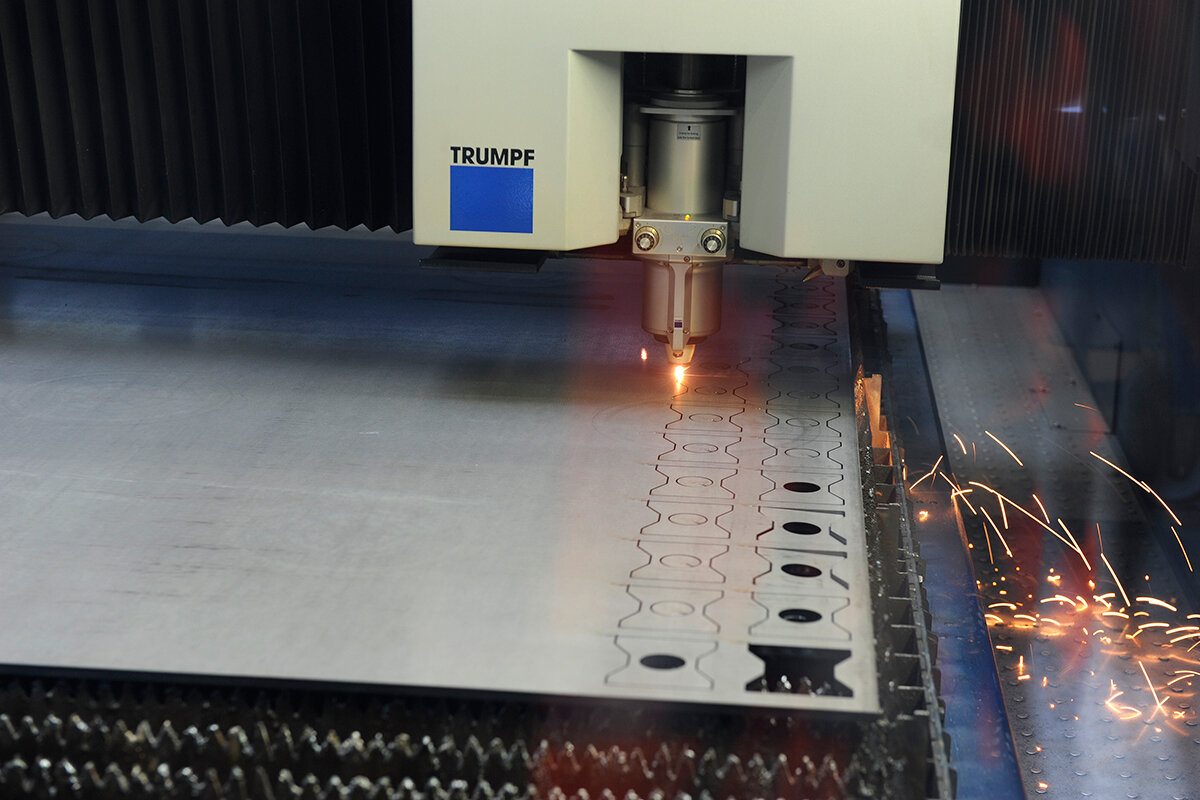
In order to cut glass, wood, steel and other materials as accurately and accurately as possible, special equipment is used. To date, laser machines are considered to be the most efficient and modern devices. Initially, they had an exclusively industrial scope, but at the moment they can also be used in a household workshop.
Laser cutting is a method of cutting material, during which a focused powerful laser beam burns through the workpiece surface to be processed.Due to its small thickness, special angle of direction, coherence and monochromaticity, the laser beam cuts the material evenly, and this process produces a minimum of waste, which is then blown out by a jet of air.
Due to its increased accuracy, laser cutting significantly speeds up and simplifies the processing of various workpieces, while creating a minimum of defects and scrap. The increased demand for such equipment is not surprising, because due to the increased productivity, the high cost of the machine will pay off quite quickly and more than.
Burning the workpiece directly eliminates contact with its work surface. From this it is clear that it is possible to process not only hard alloys (brass and copper, aluminum and steel), but also rather fragile raw materials, such as wood or plywood, as well as glass. Almost complete automation adds to the efficiency of the whole process. It is already difficult to imagine a modern laser machine without CNC, and its computer control has become commonplace today.
Content [Hide]
- 1 Laser machines: general information
- 2 The main stages of the laser machine
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of laser cutting
- 4 Technical characteristics of the main types of laser systems
- 5 Existing types of laser machines
- 6 Existing types of tables for machine tools
- 7 Approximate order of use
- 8 Some nuances of setting up the device
- 9 The main significant parameters when choosing a laser device
- 10 Price dependency
- 11 Ranking of the best laser cutting machines for 2025
- 12 Instead of an epilogue
Laser machines: general information
They are professional equipment, the work of which is characterized by increased accuracy. The device is equipped with a powerful laser, which easily cuts through the surface, divides them into separate elements. The resulting cut is particularly smooth and does not require an additional processing step. Also, with the help of such machines it is convenient to engrave, cut out various patterns, and even weld small parts.
Device and working elements
Externally, the design is not particularly complex and consists of:
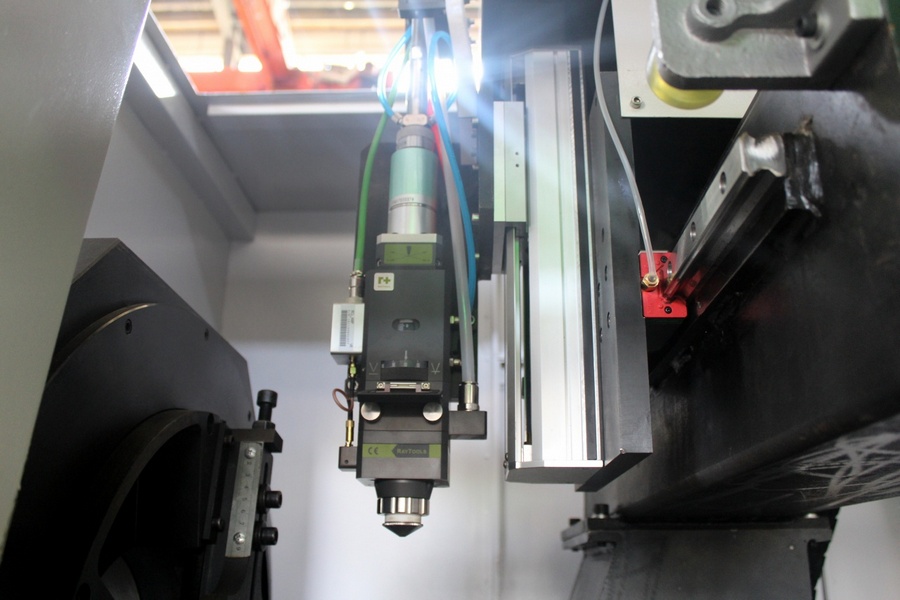
- Coordinate table - he is responsible for the final quality of the manufactured product. On it is a housing on which the movable guide parts are placed. As a drive, ball screws or toothed belts can be used. In laser machines for metal, one more control element is additionally used - the controller.
- "Flying" optics - it consists of a set of mirrors, each of which has a coating in the form of a special composition that reduces the scattering of the energy beam. A lens is also installed there, which is responsible for focusing the beam into a small spot with a diameter of no more than 2/10 mm.
- Laser lamps - it is the main radiating element (sealed glass variations are usually used). The radiation that is reflected from the mirror optics and further focused by the lens, and performs the main work - burning.
- Additional devices - usually these include an air compressor and the main cooling system.
The lens is the main working element
Through it, the beam generated by the lamp is focused and directed to the material being processed. Different lenses have different focal lengths, focal depths (responsible for the maximum thickness of the incision), and the diameter of the focused spot. There are telephoto (+100 mm), medium-focus (up to 50 mm) and short-focus lenses (up to 38 mm). As the name implies, they differ in the length of the focusing distance. Thus, telephoto lenses are able to cut through thick and hard surfaces (metal) efficiently, while others can efficiently produce chiseled work. According to the current classification, each lens variation is used for its type of work:
- Short-focus - do an excellent job of engraving and cutting out detailed objects (for example, seals), and it is also convenient to cut materials of low density (plywood, chipboard, plexiglass) with them;
- Medium-focus lenses are often called the “golden mean”, because they are able to engrave with high quality and cut through workpieces of medium density up to 8 mm (this thickness can be compared with the density of wood);
- Telephoto lenses are great for working with thick materials (in addition to standard metals, acrylic and wood with a thickness of up to 250 mm can be mentioned).
The lenses themselves can be made on the basis of various bases, the most popular of which are gallium arsenide and zinc selenide. It is worth noting that the former belong to industrial designs and are used in machine tools with a power of more than 130 watts.
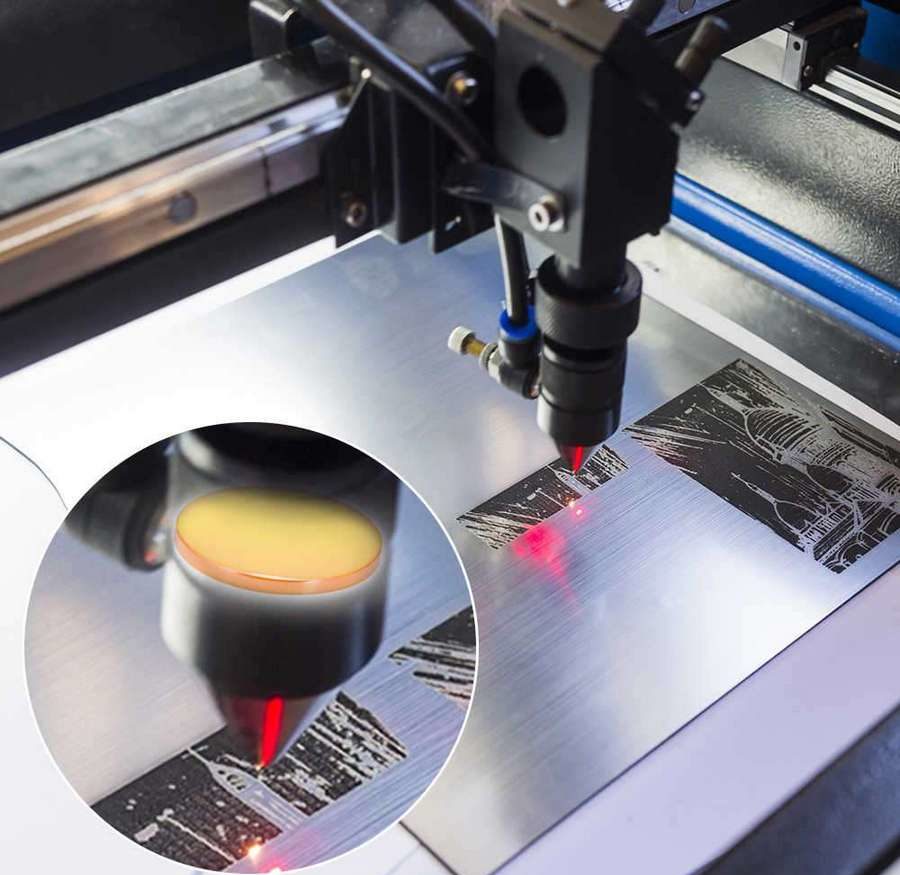

The main stages of the laser machine
First, a special drawing is prepared, where the coordinates of the desired cuts are indicated - this drawing is loaded into the operating program of the machine.After that, the working process begins directly: the machine automatically directs the beam to a given place and it is strongly heated. Glass and metal melt under the influence of elevated temperature, and the tree burns out. In a strictly designated place, the surface to be machined is accurately cut in accordance with the specified parameters.
Advantages and disadvantages of laser cutting
The undoubted advantages are the following:
- Laser cutting is capable of processing various materials;
- The absence of direct mechanical contact virtually eliminates the risk of damage to the treated surface;
- On the machine it is possible to perform work of any degree of complexity, while obtaining perfectly even cuts and lines is guaranteed;
- The work performed is characterized by high productivity and speed;
- The process itself is carried out silently, there is no large amount of dust and debris.
The disadvantages of working with a laser include:
- The stamping method of processing blanks is much cheaper than the laser one;
- During the processing of wooden surfaces, traces of a dark color remain in the places of its contact with the laser spot;
- Laser machines themselves (especially industrial designs) are very expensive;
- There are limitations in the area of the thickness of the working surface of materials.
The range of products that can be made on a laser machine is very wide, the unit is perfect for manufacturing:
- Various stencils and plywood blanks;
- Metal constructors and their individual elements;
- Seals and stamps;
- Street signs and road signs;
- designer postcards;
- Souvenir items with engraving;
- Decor elements containing carved patterns;
- Decorations and screens;
- Models for architectural projects and much more.
Technical characteristics of the main types of laser systems
Depending on the material being processed, they can be divided into:
- Lamp-pumped repetitively pulsed solid-state lasers (output power: 50 - 1000 watts) are used for cutting thick metals;
- Diode-pumped DPSS solid-state lasers are used for medium thickness metals;
- Continuous infrared CO2 gas lasers (output power up to 400 watts) are used to work with non-metallic workpieces (rubber and polymers, as well as wood);
- Continuous gas CO2 lasers (output power - from 0.7 to 6 kilowatts) are suitable for working with alloyed steel, ferrous metals, some types of metal alloys, as well as for non-metallic materials;
- Fiber lasers (output power from 0.4 to 15 kilowatts) - for spot cutting.

At the moment, the use of laser equipment cannot completely displace classical methods of metal cutting from the market. Therefore, their effective use becomes possible only when the processed material is selected correctly, based on the capabilities of the equipment, and when using the traditional method becomes laborious or completely impossible.
Existing types of laser machines
This equipment can have both universal and specialized purposes. However, all equipment is usually divided by power and size:
- The desktop device is characterized by low power (less than 80 watts);
- Professional already has a lot of power (from 80 - 195 watts);
- Production samples can reach power up to 1000 watts.
Depending on the working environment, lasers can be classified into
- Solid state - they are equipped with pump lamps, flash lamps, a working case and several mirrors;
- Gas - they have a system for supplying inert gases, as well as a glass flask in which the radiating tube is located;
- Gas-dynamic - they have a special nozzle for accelerated gas supply and an additional cooling system.
Existing types of tables for machine tools
The desktop is one of the main elements in the design of the machine, so the quality of work will directly depend on its choice:
- Lamellar tables - they are often found in the basic configuration, they are extremely convenient to remove and clean. However, they are not well suited for fine detail work or fabric work. Also, they are not at all designed for processing special and thin materials, such as paper or cardboard.
- honeycomb tables - their coating is very, very suitable just for cutting small elements, because it is very dense and does not allow the workpieces to fall to the floor. He will perfectly cope with cutting thin material - paper, cardboard, fabric. Unlike lamella tables, the workpiece does not sag on it.
- Conveyor tables - they are specially designed to work with material in rolls, which include paper and even leatherette. On them, the supply of blanks is provided in a continuous mode, which greatly simplifies the work of the user.
Approximate order of use
The basic rules for operating the machine are quite simple, but it is still necessary to know the step-by-step procedure so as not to get confused later:
- First you need to choose a pattern that will be cut out;
- Then you should load the image (photo) into the operating program of the device, at the same time checking the cleanliness of the working surface of the lens.If contamination occurs, then the lens must be wiped with a cotton swab dipped in alcohol;
IMPORTANT! It is impossible to wipe the lens with vodka, since the essential oils present in its composition form a thin film on the lens when dried, which will lead to beam scattering!
- After turning on the unit, you must wait until it warms up;
- Next, you should select the processing method: "raster" for engraving and "vector" for cutting;
- Then you need to determine the line width for the cut (it is worth remembering that wide lines are drawn for a long time);
- At the end of all operations, the process will begin to be carried out, while the manufacturing time will depend on the material being processed and the set speed mode.
Some nuances of setting up the device
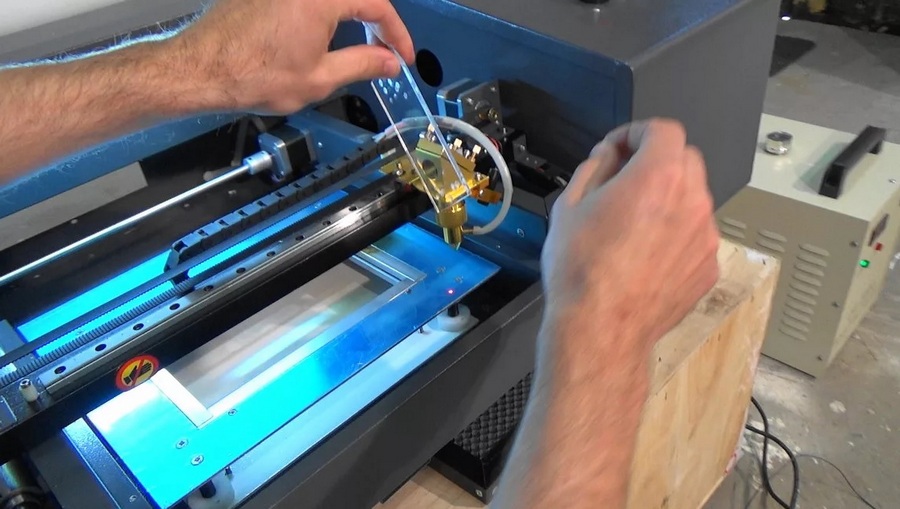
It must always be remembered that the laser machine is a complex technical equipment, so its setting must be extremely accurate. The adjustment is carried out according to the light beam, and for the duration of this procedure, the working element is replaced with a conventional laser pointer. The procedure will include the following steps:
- Correction of the laser tube - a transparent adhesive tape is glued to the main mirror, and the position of the tube itself is set in such a way that the beam hits directly into its center;
- Then the adhesive tape is glued to the second mirror, and the main one is adjusted. As a result, the laser pointer mark should always be in the center, regardless of the distance. The direction of the beam is changed by turning the screws;
- Next, the third mirror is pasted over with adhesive tape and the above procedure is repeated, but only for the second optical element;
- The third mirror is configured by placing a "target" on the desktop. In this case, the size of the spot must correspond to the size of the outlet nozzle. Adjustment is also made with screws.

The main significant parameters when choosing a laser device
Modern manufacturers are constantly and actively working to modernize and reduce the cost of existing technologies, so the market is constantly replenished with new samples. Based on the required tasks, when choosing a unit, close attention should be paid to the following factors:
- Production volumes - domestic single use or there is a need on an industrial scale;
- Machine dimensions - it all depends on the size of the available premises;
- The main type of future materials - fiber-optic lasers are suitable for metal and plastic, and carbon dioxide models are usually used for fabric and paper, rubber and wood;
- Characteristics of the emitter - power will indicate the speed of work;
- The possibility of moving the desktop - the thickness of the processed workpieces will depend on this parameter;
- Number of cutting heads – having more than one cutting head means increased productivity. For an engraving machine, they need at least two;
- Equipped with a video camera - with its help it is easiest to transfer the necessary image to the operating program of the device;
- Roll feed mechanism - they will need equipment if it is supposed to work with materials that can be rolled into a roll (paper, fabric, etc.);
- Additional accessories - this may include an additional table surface, an external cooling device, a device for turning, the ability to replace the laser tube with a higher power element, etc.
Price dependency
Often, in the market of laser machines, one may encounter the following situation: it would seem that devices that are identical in terms of technical characteristics should and cost the same, because they can even have the same desktop size? But the cost, first of all, will be made up of the overall configuration and the quality of individual parts. And these include:
- Frame;
- Table size;
- beam tube;
- heating block;
- Power supply unit;
- Engines and other control elements.
Also, additional options will have a significant impact on the price, such as a residual current device, the presence of an exhaust hood, the presence of a rotary device, the presence of a camera, etc.
It is worth mentioning that for complex technical devices, the name of the manufacturer always and everywhere plays an important role. Indeed, small, unknown companies can attract a potential buyer with extremely budget prices for their equipment, but it is difficult to find truly good equipment among such samples. And when purchasing a laser device from such companies, the user risks paying a double price, which will result in frequent repairs.
You can visually distinguish a good model even just by looking at the case. If it is made of thin sheet metal, cheap articulated shaft guides are installed in it, then such a machine is hardly adapted to work at high speeds. A large acceleration will create additional vibrations, which will inevitably lead to a violation of the correctness of the cut lines or the production of uneven engraving. It is also worth paying attention to the age of the manufacturing company - figures of 3 to 5 years are considered optimal. An age of 9 years or more already speaks of a well-deserved place in the market.And additionally it is worth discussing service issues with the seller - if a lifetime warranty or at least a 5-year service period is offered, then such a seller is trustworthy.
Ranking of the best laser cutting machines for 2025
Budget models
2nd place: WATTSAN MICRO 0203
votes 4
An excellent example of a home machine, designed exclusively for decorative and applied purposes. With it, it is easy to cut out patterned details from thin-sheet plywood or to make ornaments on plexiglass. Due to its extremely small dimensions, it does not even require a separate room for its installation.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | Great Britain |
| Beam power, W | 40 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 28 |
| Cost, rubles | 55000 |
- Small dimensions;
- Economic cost;
- Sufficient thickness of the processed material (5-12 mm).
- Narrow scope.
1st place: ZERDER FLEX 1060
votes 3
Model from a fairly young, but already becoming popular German company. It has rather large dimensions and has a relatively high positioning accuracy of the laser beam. Due to the increased working surface, it can work with large workpieces.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | Germany |
| Beam power, W | 80 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 77 |
| Cost, rubles | 120000 |
- Large desktop;
- Low price;
- The laser tube is rated for 6000 hours.
- low power laser.
Middle class samples
2nd place: MCLASER 4030 METAL
votes 1
A versatile machine capable of working with both metals and thinner materials.With a very powerful laser, it can also be used in domestic conditions, due to its relatively small dimensions and weight (it can be installed in a home workshop). However, the desktop area is small - 40 by 30 centimeters.
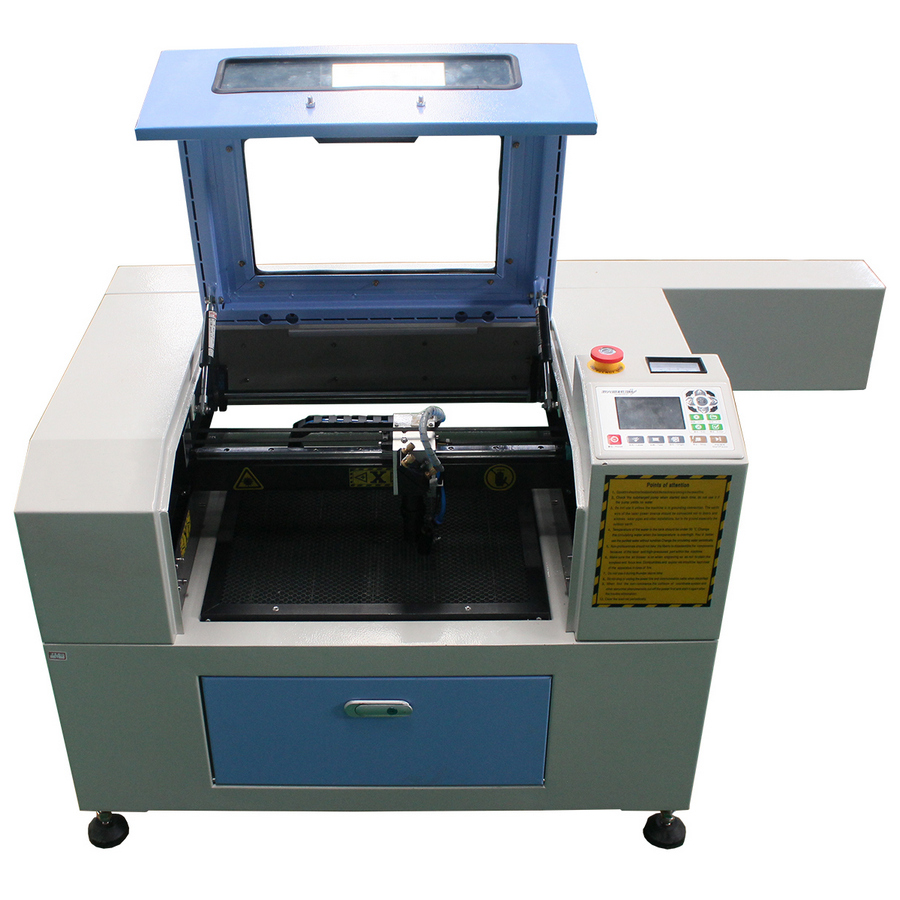

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Beam power, W | 120 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 80 |
| Cost, rubles | 405000 |
- Excellent quality of components (despite Asian origin);
- Universal model;
- Ability to cut metal up to 2 mm thick.
- Small desktop.
1st place: RABBIT FB 2030
votes 1
A wide-format unit positioned on the market as a professional model. It has a high cutting speed, the desktop area is 2 by 3 meters. The design has two powerful lasers and a system of gilded mirrors. Perfect for a highly specialized workshop. The service life of the laser tube has been extended to 6500 hours.
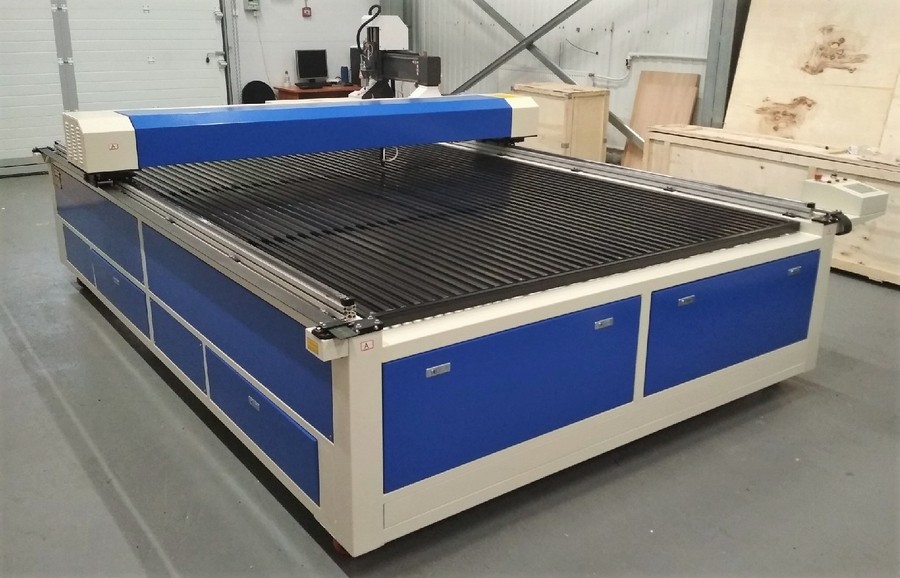

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Beam power, W | 200 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 450 |
| Cost, rubles | 1000000 |
- Multifunctionality;
- Increased working surface;
- Permissible thickness for fragile materials - 28 millimeters!
- Large dimensions;
- High price.
Models from the premium segment
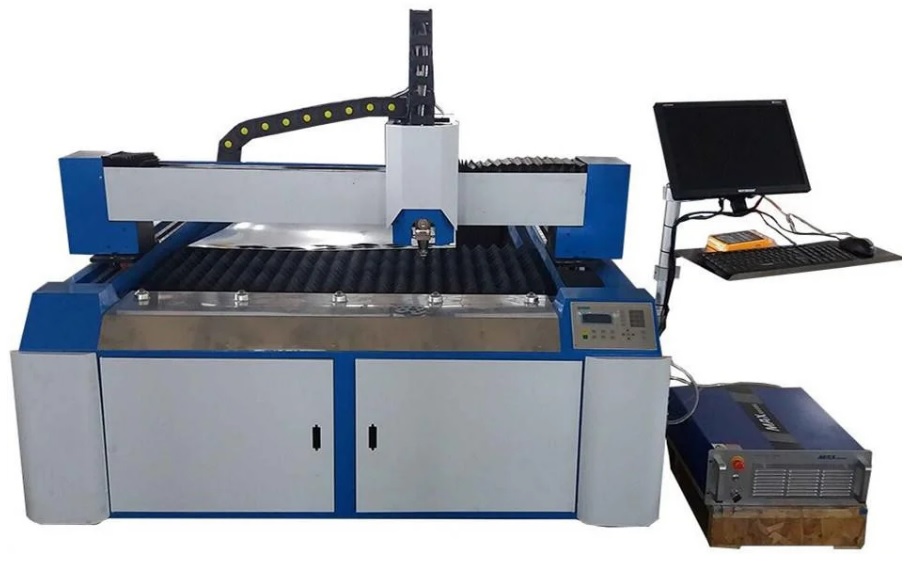
2nd place: MCLASER 1530 750W METAL
votes 0
Very powerful machine, oriented directly to work on thick metal alloys. Able to cut workpieces up to 10 millimeters thick. The working surface is large enough - 1.5 by 3 meters. Differs in the increased productivity and speed of work.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Beam power, W | 800 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 750 |
| Cost, rubles | 4000000 |
- Radiant tube life extended to 10,000 hours;
- The kit includes a separate operator panel;
- Power increased.
- Great weight and dimensions;
- Very high price.
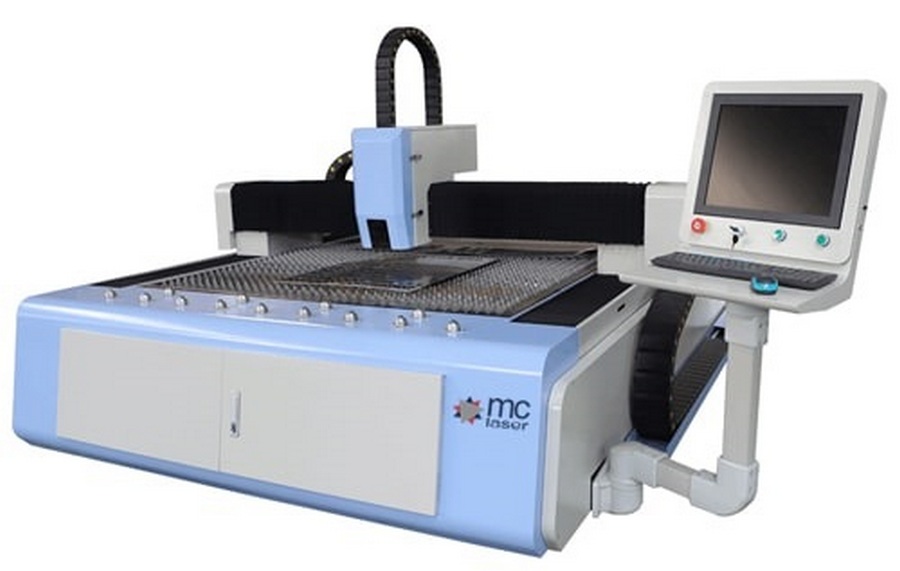
1st place: Fiber FB1325
votes 1
This laser machine has a high-power fiber optic generator, Western European linear guides, and a high-precision CNC system in its design. The device is capable of working on thick metals and their alloys. In general, it is characterized by high cutting efficiency and economy.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Beam power, W | 950 |
| Power supply, V | 220 |
| Weight, kg | 800 |
| Cost, rubles | 4700000 |
- Completely professional model;
- Versatile and multifunctional;
- Adopts economical cutting technology.
- Not found (for their segment).
Instead of an epilogue
The analysis of the market showed that the leaders in it are by no means Western companies. The Russian buyer prefers to purchase analogues of Asian production, since the components used to assemble them are still produced in Europe. And this already allows us to talk about the overall quality. At the same time, most Chinese firms do not have their own service centers in the Russian Federation, which means that there may be some problems with repairs. However, since the beginning of 2019, this situation has begun to improve - authorized centers have appeared in Siberia and the Far East, which provide the services of field specialists in the regions of Russia (even as part of a warranty service).
new entries
Categories
Useful
Popular Articles
-

Top ranking of the best and cheapest scooters up to 50cc in 2025
Views: 131656 -

Rating of the best soundproofing materials for an apartment in 2025
Views: 127697 -

Rating of cheap analogues of expensive medicines for flu and colds for 2025
Views: 124524 -

The best men's sneakers in 2025
Views: 124041 -

The Best Complex Vitamins in 2025
Views: 121945 -

Top ranking of the best smartwatches 2025 - price-quality ratio
Views: 114983 -

The best paint for gray hair - top rating 2025
Views: 113400 -

Ranking of the best wood paints for interior work in 2025
Views: 110326 -

Rating of the best spinning reels in 2025
Views: 105334 -

Ranking of the best sex dolls for men for 2025
Views: 104373 -

Ranking of the best action cameras from China in 2025
Views: 102221 -

The most effective calcium preparations for adults and children in 2025
Views: 102015









