Rating of the best ointments for joints for 2025
Diseases of the joints, as well as the musculoskeletal system (ODA), can lead to a decrease in physical activity, which will clearly affect the overall ability to work. Of course, any disease undermines the quality of human life, but it is the disease of the joints that must be detected in the early stages by correctly diagnosing the symptoms. The best drugs will be those that have proven safety and a sufficient level of effectiveness. It is always worth remembering that any medicine has contraindications, so it must be taken under the supervision of a specialist doctor. We will talk about the best ointments for the joints below.
Content [Hide]
The most common joint diseases
Conventionally, they can be divided into three main groups:
- With inflammatory processes - this includes almost all types of arthritis (reactive, infectious, gouty, rheumatoid, psoriatic);
- Without inflammatory processes - arthrosis is meant here;
- Secondary - they appear together with the disease of other organs and can be attributed to them: polymyositis, scleroderma, Sjogren's disease, lupus erythematosus, oncological diseases.
The processes of inflammation cover both individual articular parts and the entire joint as a whole. Symptoms will directly depend on the cause of the occurrence, but all of it is combined under the traditional formulation of "articular syndrome". The patient will complain of limited movement, pain, and bone deformity in the affected area.
The main disease of the non-inflammatory type of ODA is considered to be osteoarthritis. It begins to manifest itself at the age of 50-60 years and up to 80% of the entire population of the Earth in this age category suffers from it. With this disease, first of all, the synovial membrane and ligaments are affected. Further, the process covers all articular parts.Without timely treatment, the bones will undergo irreversible deformation, cartilage will be destroyed, as a result of which their overall functionality will be lost, and the appearance of permanent chronic pain will become the background.
The main causes of joint diseases
The type of disease in question can be caused by the following factors:
- Age over 45 years;
- overweight;
- Bad heredity;
- Congenital malformations (dislocations, underdevelopment of bone tissue, hypermobility);
- Long-term mechanical stress;
- Excessive sports loads;
- Consequences of injuries;
- Insufficient physical activity (physical inactivity);
- Violation of metabolic processes in the body - gout, diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands, dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain;
- Decreased quality of bone tissue (various consequences of osteoporosis);
- Various viruses - "mumps", "rubella", hepatitis, HIV, adenoviruses;
- Autoimmune inflammation (the body accepts joint elements as foreign bodies and produces antibodies against them);
- Bacterial infections - gonorrhea, staphylococcal sepsis and Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis).
Specific Causes
However, there are special reasons for the manifestation of joint diseases. A prime example would be rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune inflammation, but its underlying causes are still a mystery. Even able-bodied young people are subject to it. Another example is ankylosing spondylitis (Bekhterev's disease), which is associated with immunogenetic abnormalities (to some extent even with genital and intestinal infections).
The most common specific causes of joint disease include:
- General intoxication of the body due to past diseases - pain can be caused by influenza, SARS, chickenpox, cholecystitis, tonsillitis and a worsened oncological background. Toxins begin to form in the body, which increase pain. The only treatment option is to defeat the underlying disease.
- Arthritis rheumatoid - when it occurs inflammation of the joint. As a rule, the disease begins with small bones in the feet and hands, later it moves to the parts of the ankle, knees, pelvis and hips, wrists and elbows. The disease is reactive, and the severity of pain can increase to unbearable in just a few days. A symptom may even be the usual morning stiffness of the ODA when moving, the skin becomes reddish, accompanied by general swelling. Rash occurs less frequently and body temperature rises. In more advanced cases, the joints will “wine” without ceasing, and the stiffness of movements will not go away.
- Rheumatic polyarthritis - usually this disease is detected a few days after suffering a sore throat or flu, although it may not be associated with them. The course of the disease is characterized as acute, the temperature rises against the background of general joint pain and swelling, which manifests itself symmetrically. Inflammation of the heart muscle is also possible.
- Gout - during this disease, the smallest crystals of urea get into the cavity of the joints. Usually, the disease starts with pain in the big toe, gradually developing further. It occurs in the form of attacks, most of which begin abruptly at night or in the early morning. The pains are characterized by a special intensity, and the acute period can last about a week.Periodically, attacks will be repeated, tactilely sensitive knots, tophi, will form on the joints. With gout, cartilage and ligaments are destroyed, which will eventually lead to joint deformity.
- Reactive arthritis - manifests itself some time after the cure of various infections (pseudotuberculosis or chlamydia). First of all, it affects small joints, gradually spreading to large ones. Its symptoms are very similar to gout, and correct diagnosis is possible only after a blood test. This analysis for gout will show the presence of uric acid in the blood, and for reactive arthritis - C-reactive protein. After a period of seizures, remission may occur, however, a clear time frame is difficult to establish, they can change without reason. This type of arthritis may be accompanied by diseases of the kidneys, heart or other organs.
- Arthritis psoriatic - traditionally accompanied by manifestations of psoriasis on the skin, which can make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. In its appearance, this arthritis can be symmetrical / asymmetric, both large and small joints are involved in the course of the disease. Parts of the spine are also at risk. Its symptoms can resemble rheumatism or arthrosis.
- Arthrosis - with this disease, premature degradation (wear) of the articular cartilage occurs. It can be subdivided into osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis or deforming arthrosis. It usually affects older females. During the course of destructive processes and due to metabolic disorders, the tissues surrounding the joint are attacked. Most often, the disease affects the fingers, ankle, knees, pelvis and hips.If you give them loads, then the pain will increase, but when you are at rest, it decreases. Perhaps the appearance of a crunch in the bones and swelling. In advanced cases, the gait worsens and the onset of complete immobility is allowed.
- Radiculitis - this disease is a consequence of osteochondrosis, i.e. when the distance between the vertebrae decreased, against the background of which compression of the spinal cord root occurred. Pain occurs in the back, in the neck or in the chest, which will depend on which part of the spine has undergone the development of pathology. Radiculitis pains are characterized by a special force, accompanied by a "recoil" in the limb.
- Inflammation of the periarticular tissues - this occurs with tendinitis, bursitis, periarthritis and is accompanied by inflammation of the joint capsule, tendon or ligament.
- Injuries - after injuries, the articular cartilage and ligamentous apparatus regenerate for a long time and restore functionality, so pain can not recede for a long time. Trauma becomes an "excellent" base for the development of arthrosis.
Chondroprotective ointments as the best medicine for joints
Medicines can be produced both in powders and in ointments. They have a slow action principle, contain in their structure a protein that is necessary for the regeneration of cartilage, bones and other joint tissues in the musculoskeletal system. Chondroprotectors are used as part of complex therapy for ODA diseases along with anti-inflammatory drugs. Their additional function is focused on the prevention of degenerative changes in the joints. They are considered equally effective both in the early stages of the disease and in its long course.
Hydration and nourishment of cartilage tissue is carried out due to the synovial fluid, the structure of which includes special poly- and monosaccharides. With excessive physical exertion, trauma, or systemic disease, the composition of the synovial fluid in the body changes, so it becomes less viscous and weakly supports the sliding of bones in the joints. The components of the ointment, when released into the synovial fluid, begin to restore its consistency, restoring the proper activity of cartilage cells. The result will be a reduction in joint pain while improving mobility. However, together with the use of the ointment, other restorative and nutritional measures should be practiced - physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy and the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Scope of chondroprotectors
Chondroitin and glucosamine will help protect the joint from starvation and destroy chemically aggressive substances that accumulate in inflamed places. Most specialists use them for diseases that result in necrosis of bone spongy tissue (bone heads). Thus, they should be used when:
- Bursitis (inflammation of the joint bag);
- Tendonitis (tendon dystrophy);
- osteoporosis;
- Spondylosis (spondylarthrosis);
- Osteoarthritis (gouty and rheumatoid types);
- Osteochondrosis.
Operating principle
The purpose of powders and ointments of this type is to reduce the strength of the pain syndrome, slow the progress of the disease, and improve the mobility of the osteoarticular apparatus. Especially well, these medicines have shown themselves in the treatment of large joints - elbows, knees, hips and pelvis. For example, we can give the effect of ointment for arthrosis:
- Initially, the general symptomatology decreases (the discomfort that was caused by the destruction of cartilage decreases);
- Then there is a structural modification (the cartilaginous structure is restored, and there is a systematic opposition to its future destruction).
The very same mechanics is to stimulate the growth of chondrocytes, increasing their resistance to the threat of oxidation, suppression of enzymes, whose activity is aimed at the destruction of dense tissues. The result of the action will be the replacement of defective cartilage tissues with extended stable ones, i.e. having sufficient strength to allow the cartilage to perform its former functions in full. If prophylactic use is supposed, then the ointment will enhance the anti-inflammatory effect, while reducing the likelihood of new edema formation.
All the medicines under consideration have an accumulation effect, which means a systematic action over a long time. From this it is clear that they are the best option for reducing patients' dependence on strong steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticoid agents, which can significantly increase the duration of remission. The glucosamine present in their composition counteracts the leaching of calcium from the bones, and immediately normalizes the calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
Indications and contraindications
In principle, the type of drugs under consideration can even be used to restore the periodontal tissues, and not only for diseases of the joints and ligaments. However, their main purpose is to restore and protect the damaged bone and cartilage structure.Protectors are made on the basis of natural substances that are familiar to mankind for the entire period of their existence, therefore, contraindications and side effects during their use are very rare.
Most often, people with physical labor, athletes, as well as people leading a hypodynamic lifestyle are susceptible to joint diseases. At risk are also people aged who have experienced hormonal changes (over 45 years). The presence of metabolic and autoimmune diseases (gout, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid-type arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus), coupled with being overweight, will easily become almost 100% prerequisites for the occurrence of joint diseases.
Usually, patients from these groups should use ointments (both for prevention and treatment) when the following diseases are detected:
- The first and second stages of osteoarthritis (including any manifestations of the rheumatoid type);
- When stretching the tendons and ligaments (preventing the injury from progressing);
- After complex operations and severe injuries;
- In the presence of poor heredity (a tendency to damage bone and joint tissues);
- With the specific recommendation of a medical specialist.
However, despite the almost 100% natural composition of ointments, there is a group of people who are not recommended to use them for some reason. In most cases, this is an individual intolerance, which is not so common anymore. Accordingly, before using the ointment, you should not only carefully read the instructions for use, but also consult a doctor. Nevertheless, during the period of use of the medications in question, it is preferable for the following persons to be under the supervision of a doctor:
- lactating and pregnant women;
- Children under 12;
- Asthmatics (the smell of the ointment can cause difficulty in breathing);
- diabetics;
- Allergy (especially for types of severe allergic reaction to certain types of protein);
- People with gastrointestinal problems at the stage of exacerbation (stomach ulcer or gastritis);
- Patients with kidney diseases (urinary and cholelithiasis, renal and hepatic insufficiency);
- Persons with vascular pathologies (thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, varicose veins), as well as a violation of blood clotting;
- Patients with oxaluric diathesis;
- Cancer patients (as prescribed by a doctor).
Rating of the best ointments for joints for 2025
Universal ointments
4th place: "Indomethacin ointment 10% 40g"
votes 0
This non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointment has a powerful and high-quality analgesic effect. Indomethacin should be well rubbed into the skin, because it can leave greasy marks. By itself, it is a thick yellow substance, which is used for the symptomatic treatment of pain in arthritis and arthrosis, as well as in acute injuries. It is necessary to apply the medicine 1-2 times a day, but not more than two weeks in a row, because side effects in the form of allergic reactions are possible. The recommended cost for retail chains is 142 rubles.

- Decongestant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects;
- Small course of treatment;
- Outdoor application.
- For persons over 14 years of age.
3rd place: "Nise gel 1% 20g"
votes 0
This transparent yellow gel is based on nimesulide. The drug is often prescribed, as it exhibits a good analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, but has a low risk of causing side effects, which distinguishes it favorably from similar Diclofenac and Indomethacin, because it is a more modern and selective drug from the NSAID group.The gel must be applied 2-3 times a day, and the duration of the course is 30 days. The recommended cost for retail chains is 300 rubles.
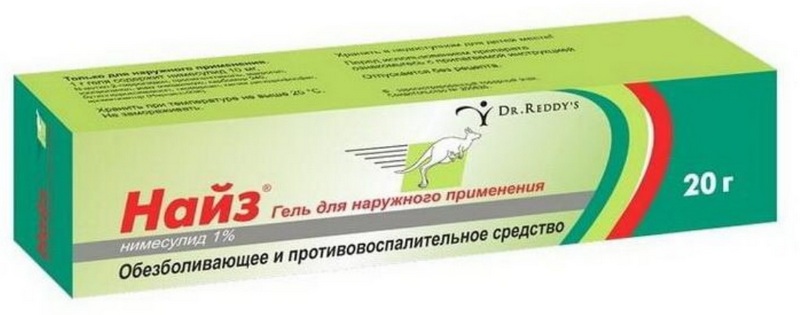
- Expanded degree of efficiency;
- Relatively short course;
- Innovative healing formula.
- Not detected.
2nd place: "Finalgel"
votes 0
The main active ingredient is piroxicam. This is a drug from the group of oxycams, which has a prolonged action, a moderate anti-inflammatory effect and analgesic activity. The ointment is used for bruises, moderate injuries, arthritis, and exacerbation of arthrosis. When used externally, the drug is well tolerated and rarely causes severe side effects. The duration of treatment is up to three weeks without the need for a break. The drug should be applied 2 times a day. The ointment looks like a transparent yellow substance and has a characteristic odor. The recommended cost for retail chains is 470 rubles.

- Overdose is not possible;
- Use by pregnant women is allowed;
- Soft action.
- Somewhat overpriced.
1st place: "Meloxicam Canon gel for external use 1% 30g"
votes 0
This is one of the best non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments. It belongs to modern painkillers with a high degree of safety, which is achieved due to selectivity. In relation to cartilage, the ointment is neutral, and with prolonged use it does not worsen the structure, unlike the same Diclofenac. Yellow gel should be applied 2 times a day. The duration of therapy is 1 month. The recommended cost for retail chains is 230 rubles.

- The best ratio of price and quality;
- The absence of a large number of contraindications;
- Directed action.
- Not detected.
Warming ointments
3rd place: "Kapsicam ointment 30g"
votes 0
This emulsion has a powerful warming and irritating effect due to the action of the medical components included in the composition - nicotinamide, capsaicin, dimethyl sulfoxide. After rubbing, the ointment begins to warm up the area of the body after 10 - 15 minutes. It is necessary to use a small amount of the product, applying it with rubbing, massage movements using the applicator included in the package, so as not to burn your hands. The duration and frequency of use is determined by the attending physician individually. The recommended cost for retail chains is 515 rubles.

- Active biological formula;
- Rapid achievement of a healing effect;
- Immediate heating effect.
- Contraindicated in children.
2nd place: "Ketoprofen gel 5% 30g"
votes 0
This is a sports cream for external use, specially designed to warm up the muscles before the start of sports activities. It is a white thick substance with a specific smell, it must be carefully rubbed in order to prevent stains on the skin. Also, the gel helps with pain in the degenerative type of articular cartilage tissue, when pain, for example, in the knee is associated with arthrosis. You need to apply it 2 times a day, carefully rubbing the thickened mass into the skin, so that no greasy marks remain. The duration of therapy with regular application of the drug is determined by the doctor individually. The recommended cost for retail chains is 228 rubles.

- Sports version of the gel;
- Narrow specialization;
- Adequate price.
- Not detected.
1st place: "Chondroitin-AKOS ointment tube 5% 30g"
votes 0
This drug consists of 2 active elements - chondroitin sulfate and dimethyl sulfoxide. The first element is a chondroprotector, takes part in the regenerative processes for cartilage and bones. Chondroitin helps to relieve severe pain against the background of pain syndrome, which can develop gradually, over the years. With the destruction of bone tissue, when there is a constant feeling of discomfort during inflammatory processes, dimethyl sulfoxide helps a lot. In persons diagnosed with arthrosis, against the background of its use, the severity of the pain syndrome subsides, as well as the effect of the action of chondroprotectors applied superficially increases. Given the complex treatment with chondroitin ointment, it can be used according to the situation - before the start of physical activity or when people with existing arthrosis need to be on their feet for a long time. As a rule, the gel is applied 2-3 times a day, rubbing well into the skin, and the duration of treatment is one month. The recommended cost for retail chains is 230 rubles.

- Complex composition;
- Minimum side effects;
- Application variability.
- Not detected.
Conclusion
The choice of a drug in the form of an ointment is best done after a diagnosis and consultation with a doctor. It is possible that a standard over-the-counter over-the-counter drug will not work or will not last long. In any case, the doctor will help develop a combined treatment regimen, based on the characteristics of each individual patient.In addition to analgesic and anti-inflammatory therapy, non-pharmacological methods can also be used, including physiotherapy exercises, orthopedic correction or physiotherapy. It is always worth remembering that the application of strongly warming ointments to a diseased joint may well backfire and worsen the situation to such an extent that a surgical operation is then required.
new entries
Categories
Useful
Popular Articles
-

Top ranking of the best and cheapest scooters up to 50cc in 2025
Views: 131651 -

Rating of the best soundproofing materials for an apartment in 2025
Views: 127691 -

Rating of cheap analogues of expensive medicines for flu and colds for 2025
Views: 124519 -

The best men's sneakers in 2025
Views: 124033 -

The Best Complex Vitamins in 2025
Views: 121940 -

Top ranking of the best smartwatches 2025 - price-quality ratio
Views: 114980 -

The best paint for gray hair - top rating 2025
Views: 113395 -

Ranking of the best wood paints for interior work in 2025
Views: 110319 -

Rating of the best spinning reels in 2025
Views: 105329 -

Ranking of the best sex dolls for men for 2025
Views: 104366 -

Ranking of the best action cameras from China in 2025
Views: 102216 -

The most effective calcium preparations for adults and children in 2025
Views: 102011









