Ranking of the best GNSS receivers for 2025

Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) receivers are special devices that are designed to receive signals from global positioning systems QZZ, COMPASS, GPS, GLONASS, as well as SBAS correction systems. These satellite devices are located in various orbits encircling our planet, or over its certain territories. Receivers (they are also satellite receivers) that have the ability to work with several systems at once are called multi-system.
These devices are used by humans to determine the exact coordinates on the ground and not only (positioning in near-Earth space is possible).In addition, they are able to measure the exact time and various parameters when moving objects (for example, direction and speed). The method by which positioning is performed is to calculate the distance between the satellite and the antenna of the GNSS receiver.
Thus, if the position of several satellites is known, then using the triangulation method it is possible to establish the position of the desired object with high accuracy, using simple geometric calculations.
The satellites themselves transmit a digital signal containing ephemeris (i.e. information about the orbit of the satellite from which the transmission is being made) and a common almanac (i.e. information about the position of all satellites in the system used), as well as updated time. The transfer of information occurs at special frequencies that are allocated for satellite transmission. As a rule, these are ranges from 1100 to 1600 megahertz.
The modern use of satellite devices has brought geodetic equipment to a whole new level - now with its help it has become easy to solve problems that are necessary not only for construction, but also for other areas of human activity. This branch of the high-precision industry is developing by leaps and bounds, various improvements are constantly appearing, so choosing the right GNSS receiver can be very difficult, due to the simple inability to keep track of new items on a permanent basis. Moreover, it is difficult to determine the receiver parameters that the user will definitely need.

Content [Hide]
- 1 Some features of the functioning of receivers
- 2 The composition of the satellite GNSS kit
- 3 The Modern Need for GNSS Instruments
- 4 Proper selection of the location of the base receiver
- 5 Initialization process
- 6 The main parameters of GNSS equipment that require close attention
- 7 Choosing the Right GNSS Receiver When Purchasing
- 8 Ranking of the best GNSS receivers for 2025
- 9 Instead of an epilogue
Some features of the functioning of receivers
GNSS receivers are not only able to determine the position both on the ground and in the air, but they can also measure the properties of objects, regardless of whether they are in a static position or moving. The essence of the calculation is the continuous measurement of the distance between the satellite and the tracking object. Every year the error of such calculations steadily decreases and, accordingly, the determination of the coordinates of the tracking object becomes more accurate. At the moment, the accuracy is already several meters.
The composition of the satellite GNSS kit
As a rule, receivers are not sold individually, but come as a set. The standard set of such equipment consists of:
- two satellite receivers;
- Field controller with installed software;
- Satellite dish type GNSS;
- Transmitting device (modem).
Current technologies have already reached such a level of development that all of the above set can be contained in one device. The main scope of these monoblocks is cadastral and geodetic works.There are devices in which the controller is placed separately and such devices are called "handhelds". It is very easy to update the operating system and control programs in them.
IMPORTANT! It is worth distinguishing GNSS receivers from tourist GPS receivers. The first are high-precision industrial equipment and are designed for use in strictly defined areas. The latter are needed for travel and tourism and have much less functionality.
The Modern Need for GNSS Instruments
Receivers for geodetic work are divided into single- and dual-system, as well as single- and dual-frequency. Almost all modern models have the ability to take into account differential corrections for the implementation of navigation tasks. When using the latest software, it is possible to plan a geodetic survey in advance, save and transfer the received data to external devices (computer), carry out primary processing of the collected information, and form a digital map of space.
Applications for GNSS equipment
Such geodetic systems are widely used at the initial stages of the construction of buildings and structures, as well as for surveying land and linking them to geographical objects. The main advantage of using these devices is their extremely fast operation time, which allows you to transfer the received coordinates for processing almost immediately. Among other things, GNSS-coordination will allow not only to build a house correctly, but also to accurately lay various communications: from water supply to the electrical network of power lines.
As a result, the priority areas can be called:
- Maintaining geodetic links at all levels - from global to classic filming;
- Study of natural phenomena occurring on the earth's surface (movement of rocks and glaciers, seismic activity and volcanism, etc.);
- Accompanying the laying of pipelines, various construction stages, as well as solving many engineering and applied problems;
- Assistance in land management and land allocation;
- Organization of leveling manipulations;
- Establishing a uniform time scale in high precision mode;
- Solving problems in the field of geoinformatics and cartography.
Basic methods of conducting GNSS-survey using receivers
Traditional the method is a statistical survey, which is optimally combined with all current sizes of bases. To do this, it is necessary to install two antennas in designated control points, they will process the entire amount of incoming data. The receivers, in turn, will track the satellites and record relatively similar parameters. For this method, it is possible to use the “fast statics” method - a small error is put into the script of the data received by the user, but all the necessary information can be collected within 15 minutes.
Kinematic the method is to quickly track several points at once, but in this case it is necessary to make sure that the equipment is at the desired point before the start of the initialization process (roughly speaking, until the next moment the satellite signal is received). If you do not make it in time, then the whole procedure will have to start all over again. This method is desirable to apply in relatively large areas, when it is possible to quickly reach the next point, for example, by car.
Also, the kinematic method can be used in extremely small areas, using the principle of "stop-go".In this case, the distance between the points should be minimal, and the main thing is that there are no objects in the area that can interfere with the passage of the satellite signal (high-rise buildings, power lines, etc.).
Among other things, real-time positioning is possible: the connection between the receiver and the satellite is practically uninterrupted. However, this method will require high energy costs, which the GNSS receiver battery may not be able to support. Typically, such solutions are used by cadastral engineers or topographers.
Proper selection of the location of the base receiver
Location is critical to a successful shoot. When performing post-processing or real-time surveys with a single or dual frequency receiver, remember that the position of the rover (moving antenna) will constantly be referenced to the position of the base. Any error in determining the coordinates of the base by a moving antenna will inevitably lead to a distortion of the coordinates of the rover itself.
Thus, two conditions must be met:
- Reliability of GNSS reception;
- Known/unknown coordinates of the base itself.
There may also be a third condition, which is the environment of the base. The base antenna should be installed as high as possible so that there are no obstacles to receive the signal on the horizontal plane and the maximum range is reached.
Condition #1: GNSS reception
It is necessary to make sure that the antenna is installed in a place where there are no obstacles for viewing a certain part of the sky in the vertical direction (we are not talking here about ground shielding obstacles located horizontally).Clear space above the base will allow collecting data from the maximum number of satellites flying over it. Such an arrangement guarantees the favorable operation of the system as a whole and the receipt of reliable data even from satellites in geostationary orbit, not to mention low-flying ones.
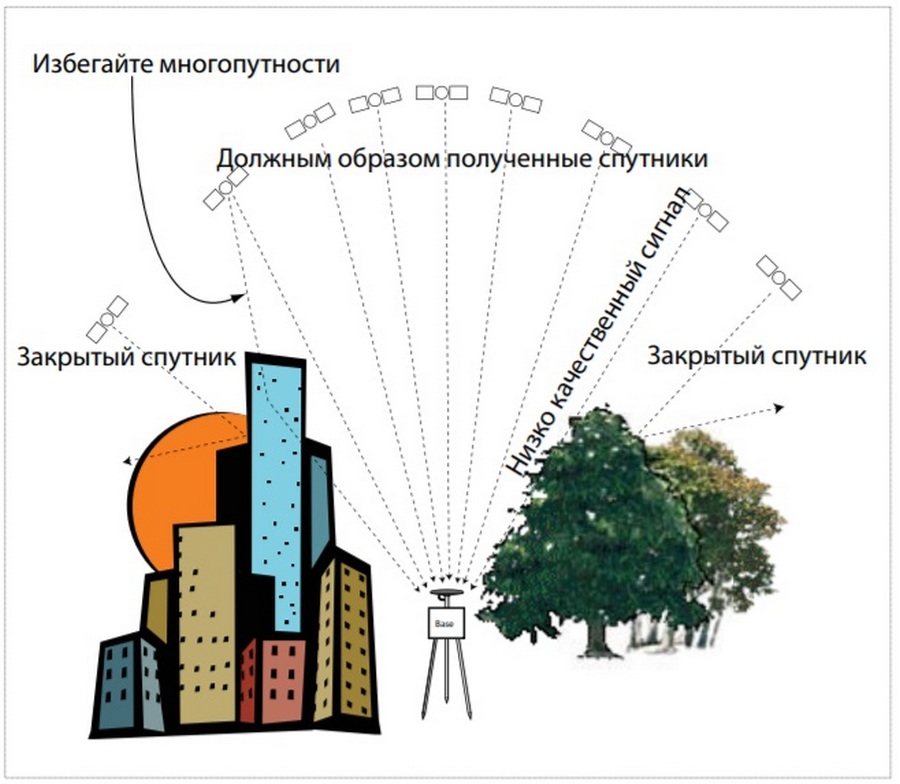
Condition #2: known/unknown base location
With some survey methods, it may well be that the exact position of the base is not known to the rover. Therefore, it is necessary to take the following measures: if it is necessary to achieve centimeter accuracy of measurements, then approximate coordinates in centimeters, which are known for the area where the base antenna is installed, should be used. If this is also impossible, then a small error should be included in the measurement scenario, which can then be eliminated by knowing the exact coordinates of the base.
Initialization process
Initialization is such a procedure, during which the receiver in real time (or the program in post-processing) can establish the ambiguity of an integer coordinate number, which is characteristic of the carrier processing phase. Such a solution is a necessary condition for the receiver and its software to obtain measurements with centimeter accuracy. Accordingly, for ultra-precise calculations, it is necessary to constantly monitor this parameter.
IMPORTANT! This process should not be confused with the initialization of the receiver by the satellite, when the primary communication is established between the devices. During the primary connection, the accuracy of the coordinates is 5-10 meters.
The main parameters of GNSS equipment that require close attention
A key role in the operation of the receiver will be played by:
- Signal processing technology and the number of channels used.When working in difficult weather or geographical conditions, the accuracy of the measurements obtained will directly depend on the stability of the signal, and hence on the number of channels used. Modern technologies for suppressing extraneous noise and multipath of some models allow you to work effectively even in inclement weather on rough terrain;
- Battery life and power. It is worth taking care of the presence in the kit of an additional battery for “hot-swap” used up. Today's standard for a single battery is one light day in the field;
- Dust and moisture protection of equipment and temperature regime of operation. The most expensive and modernized samples can operate in the range from -40 to +60 degrees Celsius. The degree of protection of the case according to the international IP standard must be indicated on the device itself. For example, IP67 means that the device can even be briefly immersed in water, and its case is completely protected from dust;
- The data format to send. For rover and base equipment, they must be the same. Any inconsistencies are immediately excluded if it is equipment from the same company. If the instrument manufacturers are different, then it is possible to use the RTCM standard, which is universal for all samples.
Choosing the Right GNSS Receiver When Purchasing
Even if the potential buyer is not a professional surveyor and has not previously dealt with such equipment, the following criteria will help you make the right choice as much as possible:
- Ease of operation and reliability. Any equipment of this type should have a simple and intuitive interface, not have too many multi-level menus and options.Simply put, the “plug-and-play” principle must be respected;
- The ability to connect the receiver to other external devices: from a modem and a computer to a smartphone;
- Supported satellite constellations. Here it is necessary to decide in which area it is supposed to work longer. For Europe, Gallileo is suitable, for Russia and the CIS countries it is better to use GLONASS, on a global scale - GPS. It is worth knowing in advance whether the selected model is multi-system - these are usually more expensive;
- The presence of a digital display. Naturally, it is better when it is present in the model. Moreover, it is preferable to choose a model with a multi-pixel LCD screen, rather than with pre-installed images. With a good non-static screen, work is much easier and more pleasant;
- Manufacturer. GNSS receivers are technically sophisticated equipment, so surveying professionals prefer samples from Western manufacturers. At the same time, they do not bypass Japan either - models from Leica (a division of Panasonic), which are characterized by increased accuracy, are especially popular.
Ranking of the best GNSS receivers for 2025
5th place: SP ProMark 220
votes 2
This model uses advanced ZED-Blade technology, which allows faster initialization and higher accuracy even with extended baselines. The receiver tries to make the most of all GNSS constellations, which means high efficiency and measurement accuracy even in difficult conditions.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Number of channels | 45 |
| Battery life, hours | 8 |
| Operating temperature, in degrees Celsius | -20 to +60 |
| Data recording frequency | 2 Hz |
| Price, rubles | 165000 |
- Innovative technologies are used;
- Extremely democratic price;
- Good complete set.
- Works only with 2 systems: GLONASS and GPS.
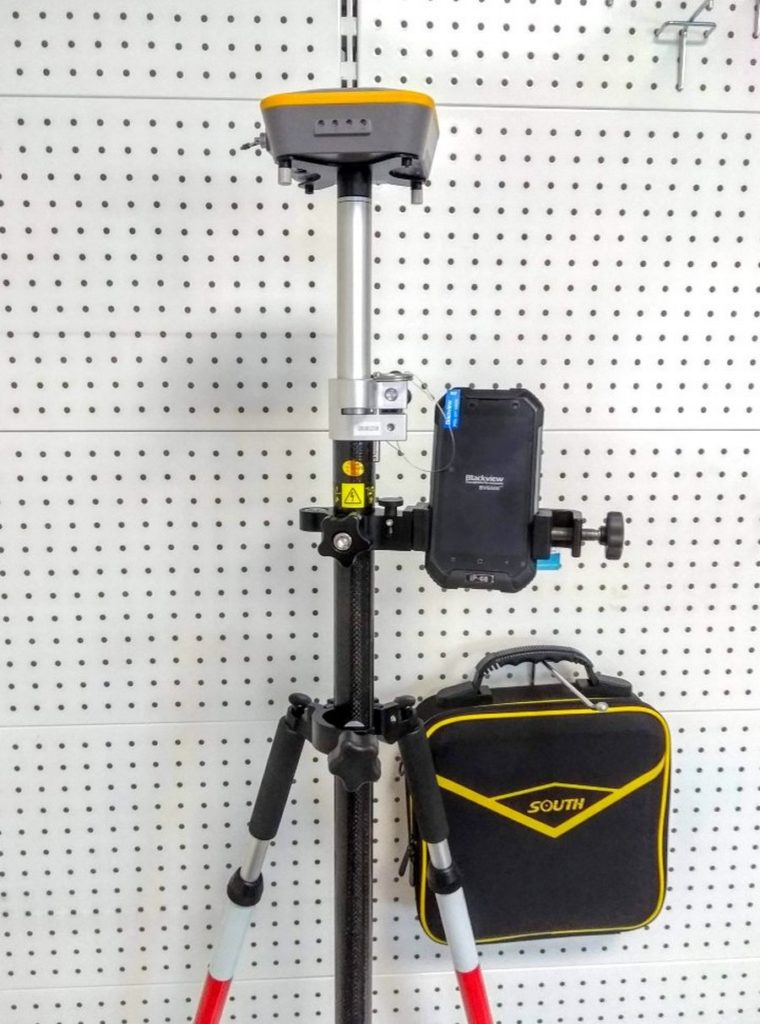
4th place: SOUTH S660 kit
votes 0
This sample is extremely easy to use, has a relatively small mass and a shock-resistant complex for all devices included in the set. The unique antenna design allows ultra-precise measurements in both static and real-time modes. The design of the device is an example of ergonomics, and the control interface is simple and intuitive. Most often used for landscape architecture.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Number of channels | 692 |
| Battery life, hours | 11 |
| Operating temperature, in degrees Celsius | -25 to +70 |
| Data recording frequency | 1-20Hz |
| Price, rubles | 340000 |
- Current value for money;
- Ergonomic design;
- Supports all known satellite constellations (civilians, of course).
- The modem only works in 2G/3G networks.
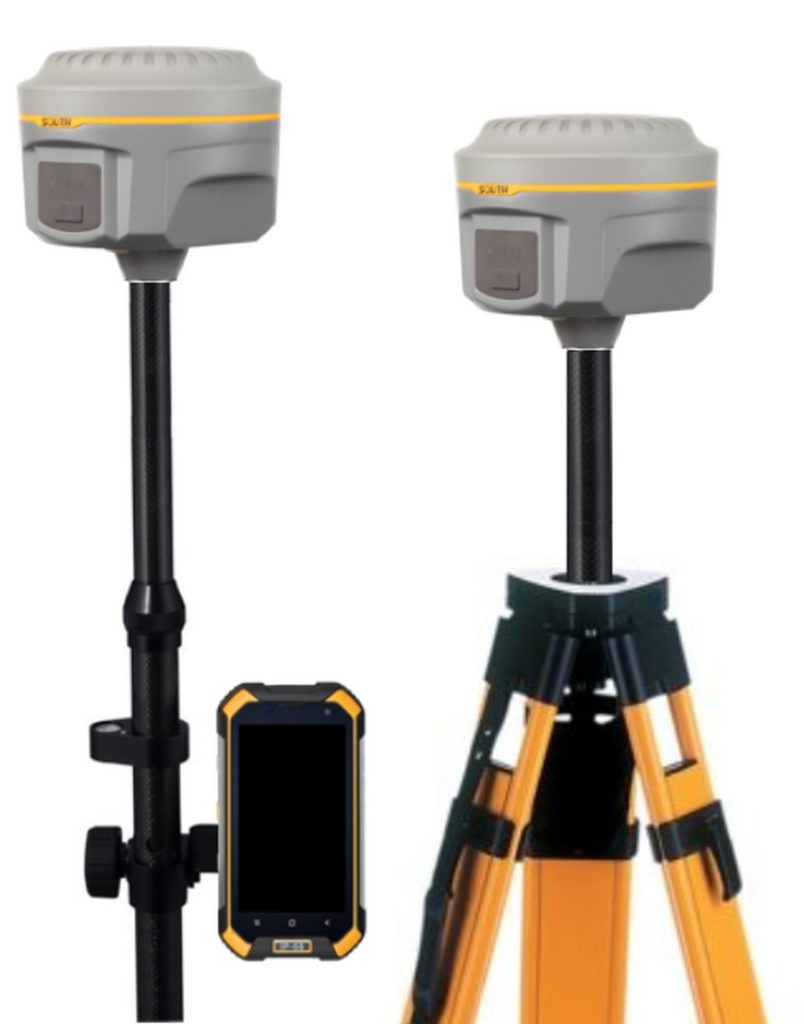
3rd Place: SOUTH Galaxy G1 Bundle
votes 0
This unit represents a new generation of receivers with a small size and advanced functionality. The receiver is equipped with automatic control of reception levels, which clearly improves the accuracy of measurements. Also, a special tilt sensor is included in the design, which allows you to eliminate centering errors and automates communications along the way. The set won the Surveyor's Best Friend 2015 Reddot Design Award.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | China |
| Number of channels | 220 |
| Battery life, hours | 7 |
| Operating temperature, in degrees Celsius | -45 to +65 |
| Data recording frequency | 1-50Hz |
| Price, rubles | 420000 |
- Almost fully automated model - in some cases, you don't even need to press a button to make measurements;
- Honored brand with an international award;
- Works under control of all existing operating systems from Microsoft (except for the 10th version).
- Not found (for its segment).
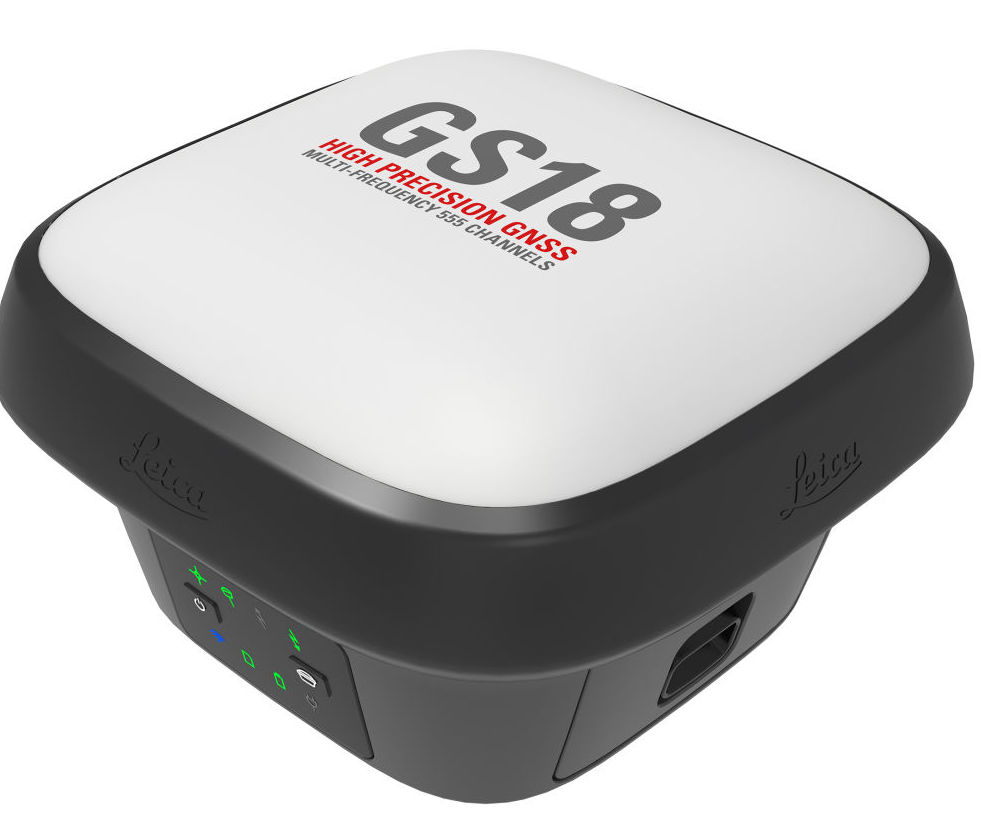
2nd place: LEICA GS18T LTE
votes 1
This model is equipped with a special compensator that smooths out inaccuracies in measurements when the pole tilt angle occurs. Thus, constant leveling of the device is not required. It is very resistant to electromagnetic influence, which makes it possible to provide stable communication with the satellite even near power lines. The case has an increased level of dust and moisture protection (IP68). Extremely unpretentious to weather conditions.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | Japan |
| Number of channels | 556 |
| Battery life, hours | 7 |
| Operating temperature, in degrees Celsius | -40 to +65 |
| Data recording frequency | 1-20Hz |
| Price, rubles | 820000 |
- Works with all satellite systems;
- No need for additional calibration;
- Data can be stored on external media (up to 8 GB).
- High price for an incomplete set.
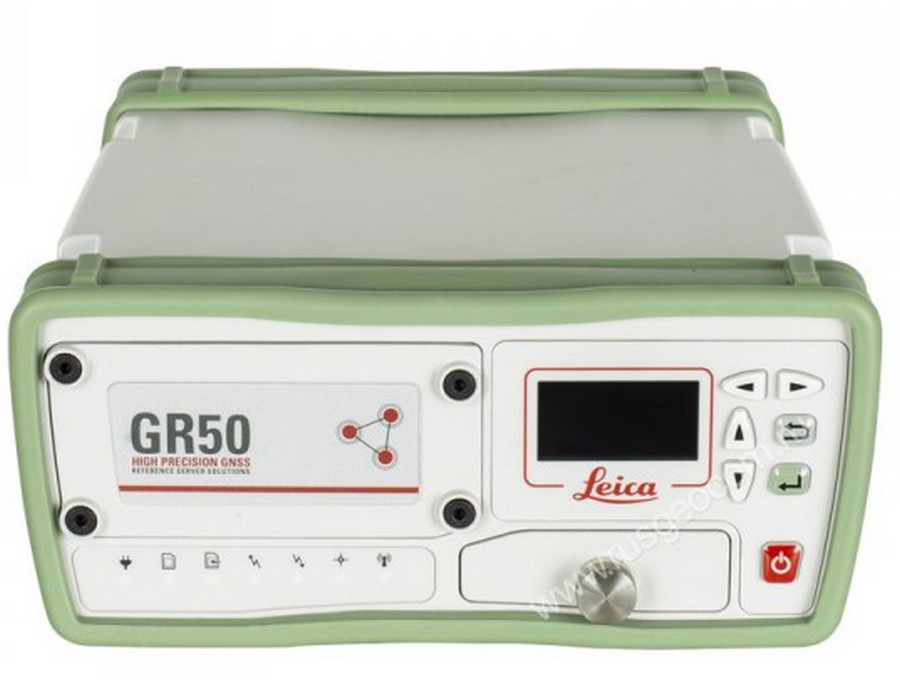
1st place: GPS Leica GR50
votes 0
This receiver can be called a "server from the world of GNSS equipment." It can work as a permanent fixed station, and as a reference (reference) model. The exceptional accuracy of the device allows it to be used in extremely precise areas, for example, when monitoring the deformations of the earth's surface.Has its own software "SmartWorks", focused on the performance of special tasks. Can work with many client rovers.

| Name | Index |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer country | Japan |
| Number of channels | 555 |
| Battery life, hours | 24 |
| Operating temperature, in degrees Celsius | -40 to +65 |
| Data recording frequency | 1-50Hz |
| Price, rubles | 1800000 |
- Multifunctionality;
- Own software;
- Support for a large number of rovers;
- Works with all satellite systems.
- Extremely high price (available only to large buyers for use in specific areas).
Instead of an epilogue
Due to the fact that the described equipment is technically complex, it should be purchased only from trusted suppliers. Moreover, professionals advise making purchases on Internet sites, because there it will be possible to save on the difference in retail prices. This circumstance is most relevant, because the price of the devices is extremely high.
new entries
Categories
Useful
Popular Articles
-

Top ranking of the best and cheapest scooters up to 50cc in 2025
Views: 131664 -

Rating of the best soundproofing materials for an apartment in 2025
Views: 127702 -

Rating of cheap analogues of expensive medicines for flu and colds for 2025
Views: 124528 -

The best men's sneakers in 2025
Views: 124045 -

The Best Complex Vitamins in 2025
Views: 121950 -

Top ranking of the best smartwatches 2025 - price-quality ratio
Views: 114987 -

The best paint for gray hair - top rating 2025
Views: 113404 -

Ranking of the best wood paints for interior work in 2025
Views: 110331 -

Rating of the best spinning reels in 2025
Views: 105337 -

Ranking of the best sex dolls for men for 2025
Views: 104378 -

Ranking of the best action cameras from China in 2025
Views: 102225 -

The most effective calcium preparations for adults and children in 2025
Views: 102019









