Rating of the best binocular microscopes for 2022

Who did not dream in childhood to see a drop of rain or a snowflake through a magnifying glass. Modern technologies have made optics affordable and high-precision. Increasing invisible objects to sizes that allow you to see the composition, structure of the sample, observe microprocesses - is this not a fairy tale that has come true. An exciting hobby can grow into a family hobby, and for some it becomes a professional choice. An enlargement device can have a certain set of parameters and vary in characteristics. Here's how to choose the right binocular microscope and live up to your expectations.

Content [Hide]
Criteria for the right choice
At the initial stage, one should decide on the scope of the tasks facing the researcher.
Depending on the upcoming direction of knowledge, devices can be divided into the following classes:
- professional;
- amateur.
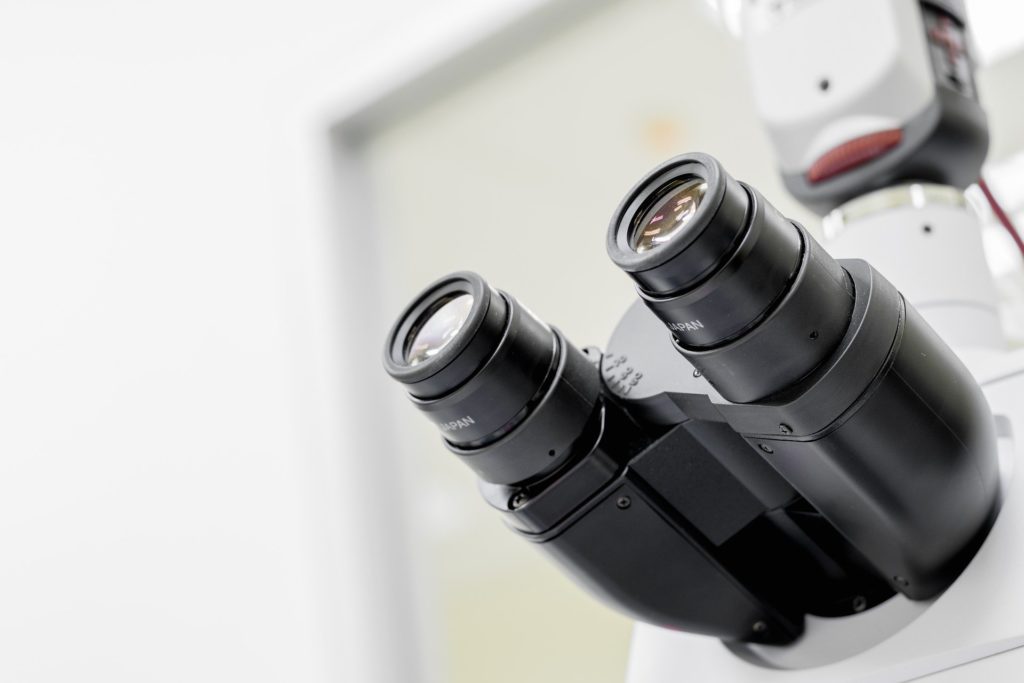
Eyepieces
The lens system, which is located on the upper tier of the tube, is directly designed for viewing images. Binocular means a pair of systems for the right and left eyes. Modern models allow you to get a three-dimensional stereo image thanks to two eyepieces and a lens. The three-dimensional image is the main advantage of a stereoscopic or binocular microscope.

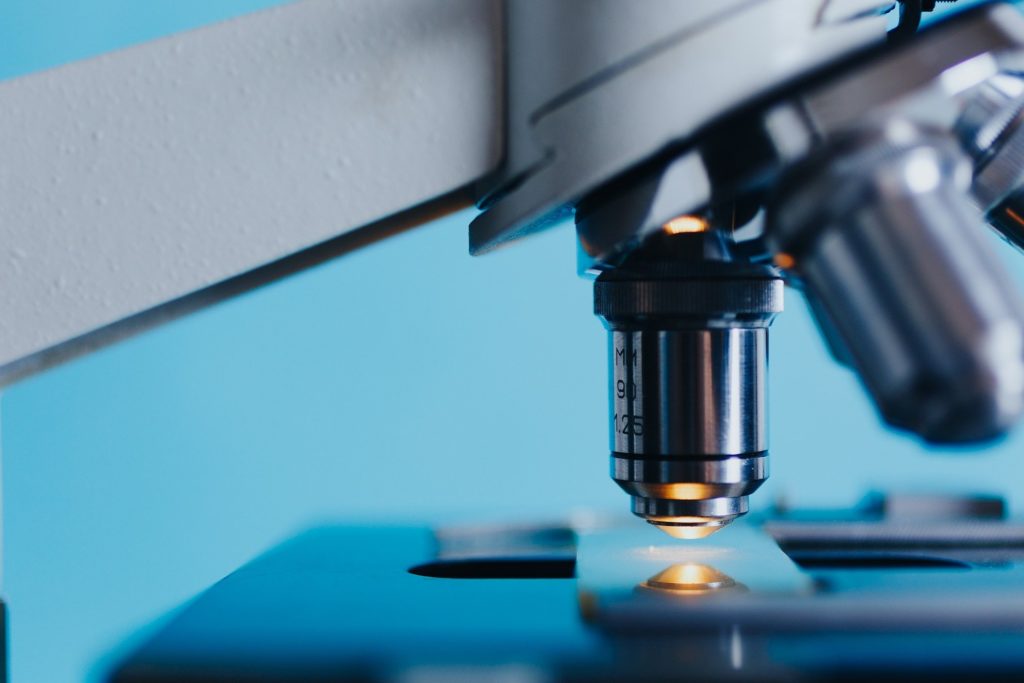
Lens
Part of the device, "looking" at the subject of research, is located above the instrument platform. Children's models are equipped with a single lens, more serious amateur and professional series have three or more units. A set of lenses is located in the revolving mechanism, where you can change during the observation. Immersion type with magnification from 40x provides for the use of synthetic oils, distilled water.
According to the type of correction, the entire range of lenses can be divided into classes:
- achromatic ones do not completely eliminate color distortions and are more often used in school and amateur devices;
- apochromatic levels out distortion by 100%;
- planochromatic ones give a clear image with the correction of the curvature of the angle of view, chromatic aberrations and are used when observing large objects;
- semiplanatic ones have distortions along the viewing edge and lower the curvature.
Increase
The magnification parameter of the device is calculated by the formula of multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece by the magnification of the objective. Accordingly, the more eyepieces and lenses the model allows, the more opportunities the microscope has. The useful magnification characteristic is calculated by multiplying the lens diameter by 1000.
| Microscope magnification | ||
|---|---|---|
| Eyepiece 10x | Eyepiece 12.5 x | |
| Lens, x | ||
| 10 | 100 | 125 |
| 40 | 400 | 500 |
| 100 | 1000 | 1250 |

Backlight type
The top location above the subject area is used when studying opaque, translucent samples. The lower illumination is located under the table and serves when observing transparent materials.
Backlight source
In total, there are 4 types of sources:
- 2 lamps - incandescent and halogen;
- mirror;
- Light-emitting diode.
In binoculars, halogen lamps with a powerful stream of white light are more often used, which are subject to regulation according to the degree of illumination.
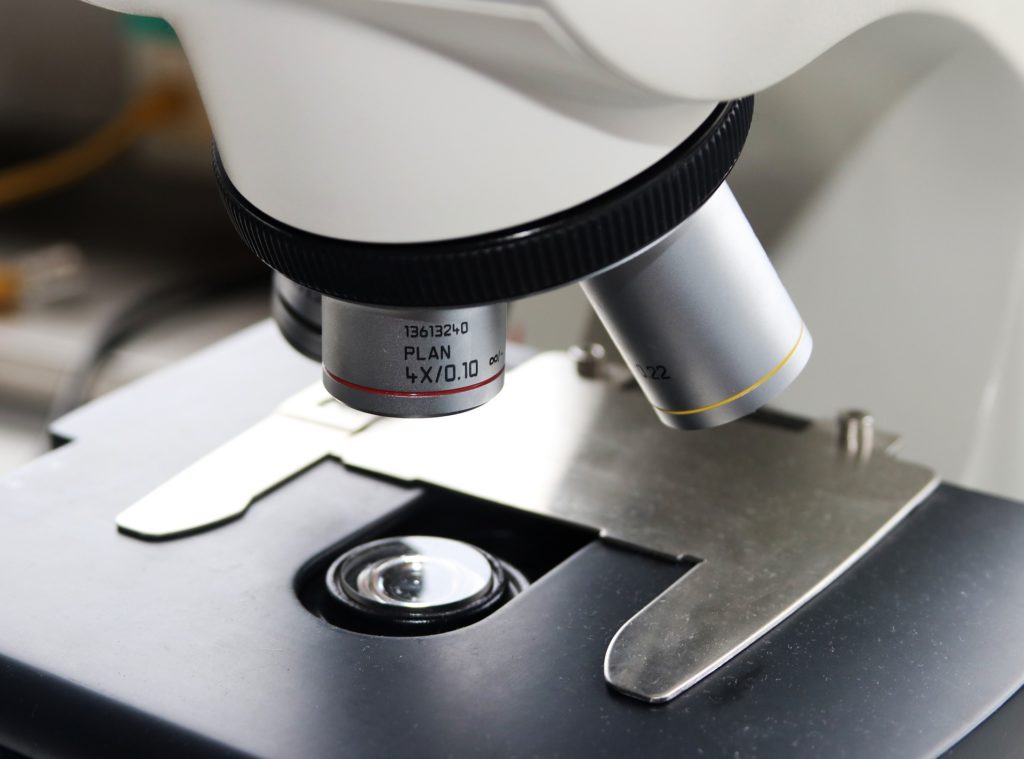
Diaphragm
The part of the device in the form of a hole, with the help of which the control over the volume of light falling on the object under study is carried out, is called the diaphragm.
A simple type of diaphragm is disc, which consists of a disc with 6 holes of various diameters.
The iris type allows you to set intermediate values and is more common in binoculars.

Focusing
The image accuracy parameter is divided into coarse adjustment within 1 mm and fine adjustment with a range of 0.01÷0.05 mm.
Additional features
Image requirements are changing rapidly.A researcher of any age seeks not only to comprehend the secret processes of the microworld, but also to capture them in a photo or video. The presence of a digital camera allows you to display a picture, dynamic changes on external screens, both television and laptop monitors, PCs.
Of interest is the adapter for smartphones, with which the mobile device is attached to the microscope. In this case, the video eyepiece changes place with the camera, the picture is displayed on the screen. There are special applications for this purpose.
Micropreparations can be purchased in the form of specialized kits with coloring in the necessary solutions, demonstrating the detailed structure of materials and objects.
Price
Children's models can be purchased with a starting price of 4000 rubles. Amateur and professional instruments for laboratories reach the upper price bracket of 160,000 rubles. Specialized optics of the highest class of accuracy and serious capabilities can cost several million rubles.
Errors when choosing
It is important to remember that for children, a magnification of 650x and the presence of a lower illumination will be sufficient.
Binoculars claim to be of a professional level and to equip laboratories where magnification of 1000÷1600x, precise focusing, and a movable object platform are required.
Excellent in all respects, optics from Carl Zeiss, Nikon belongs to the class of highly professional devices and has a price of 1,000,000 rubles.
Overview of the best binocular microscopes
Binoculars from a foreign manufacturer
BRESSER 57-22100 Researcher Bino
votes 1
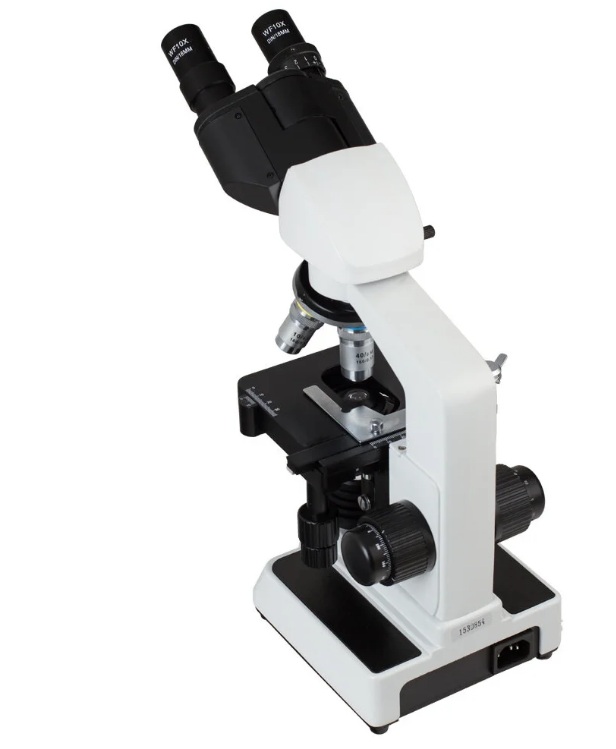
The biological microscope for laboratory research and observation has a lower illumination, 4 lenses with smooth replacement.
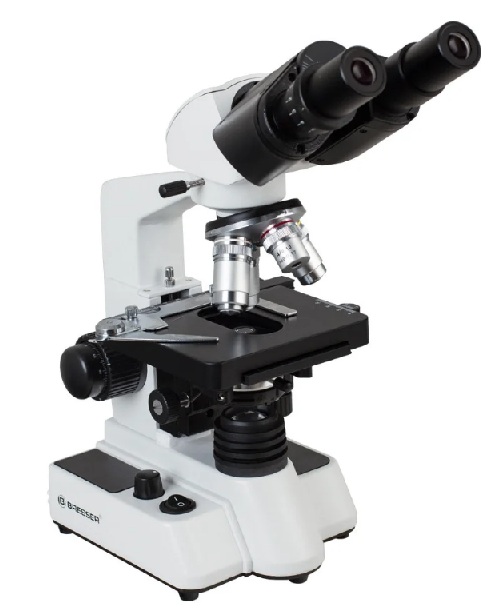

- high-precision focus;
- with a tilt angle of 30°;
- oil immersion method available;
- with precise positioning of the material;
- the presence of a diopter setting;
- does not require glasses for visual impairment;
- with a change in interpupillary distance in the range of 53-75 mm;
- lenses with optical glass;
- with adjustable backlight brightness;
- the possibility of studying opaque particles due to the high brightness;
- connecting the backlight using a complete adapter;
- the presence of clamps on the table;
- complete with immersion oil and protective case;
- the presence of a blue light filter;
- metal case;
- works from the network.
- the price is above average.
Celestron LABS CB2000CF 44231
votes 0
The device with a quick adjustment of illumination by means of a halogen illuminator of the transmitted light beam gives a bright, natural color solution.
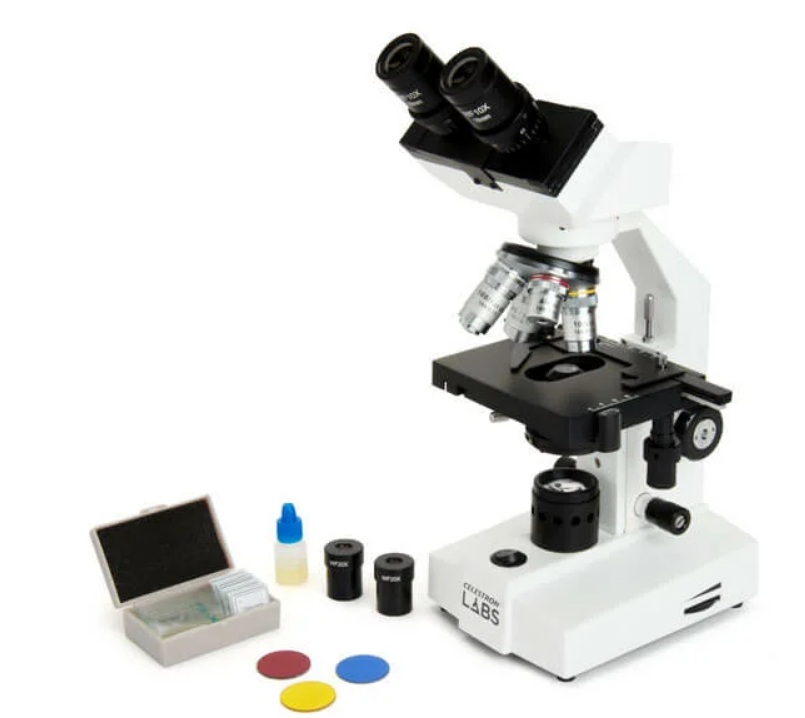
- with 2 sets of wide-angle type eyepieces;
- the presence of 4 achromatic lenses;
- with a wide range of magnification;
- the ability to install additionally purchased lenses, eyepieces;
- it is allowed to install a video camera “on a digital”;
- with all-metal body;
- high-precision focusing coarse and fine adjustment;
- glass high-quality optics;
- excellent image;
- long service life guarantee;
- with diopter adjustment in the eyepieces;
- completed with 10 micropreparations;
- two-coordinate table with applied verniers;
- the presence of coaxial handles;
- backlight control with iris diaphragm and Abbe condenser;
- recommended for educational and medical institutions, laboratories;
- there is an online purchase;
- change in interpupillary distance in the range of 48÷75 mm.
- no.
Crystallite ST-60-L
votes 3
The stereo microscope for professional work is suitable for radio editing manipulations.

- wide-field eyepieces;
- the presence of rubber eyecups;
- nozzle inclination 45°;
- adjustment of interpupillary distance, range 54-75 mm;
- with diopter adjustment;
- cold light from the ring LED illuminator;
- small weight 5 kg;
- powered by 220V;
- with an increased working distance of 10 cm;
- budget class.
- question of durability.
Eschenbach 10-20x
votes 0
A stereoscopic device on a clamp from a German manufacturer is used in the study of volumetric material by the type of reflected light.
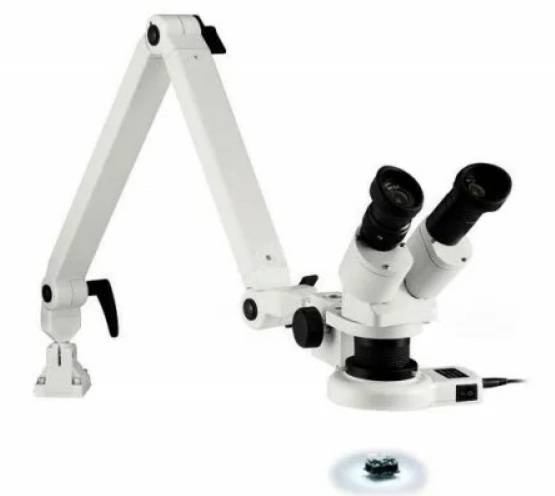
- recommended for criminologists, restorers, microchip engineers for clear and scrupulous manipulations;
- additional equipment with a 0.5x lens;
- the famous quality of the world-class manufacturer;
- individual diopter adjustment is available;
- the angle of inclination of the tube can vary;
- with wide-angle eyepieces;
- lighting is subject to regulation;
- free movement thanks to the spring connection of the metal lever on 3 locking screws;
- the presence of a table clamp;
- with tubes tilted at an angle of 45°;
- reliable focusing mechanism;
- with interpupillary distance in the range of 54-74 mm.
- without an object table.
Saike Digital SK2126S
votes 1
The binocular is very popular among radio installers who perform restoration and repair work with the need for a high-resolution stereo image.

- pancratic system of magnifications of 7-45 times;
- tight fit of the linings with the exception of dust and small particles;
- with diopter correction of wide-field eyepieces;
- adjustment of the interpupillary distance from 55 to 75 mm;
- studies using the bright field method;
- the presence of stepless zoom adjustment;
- zoom with a multiplicity of 1˸6.4;
- nice white body;
- with protective glass included;
- the optical head moves freely on a tripod and adjusts according to the size of the object;
- an annular LED illuminator with cold shadowless light was used as a light source;
- excellent reviews of specialists-repairers of electronic equipment.
- missing.
Devices from a domestic manufacturer
Micromed MS-1 var.1C
votes 0
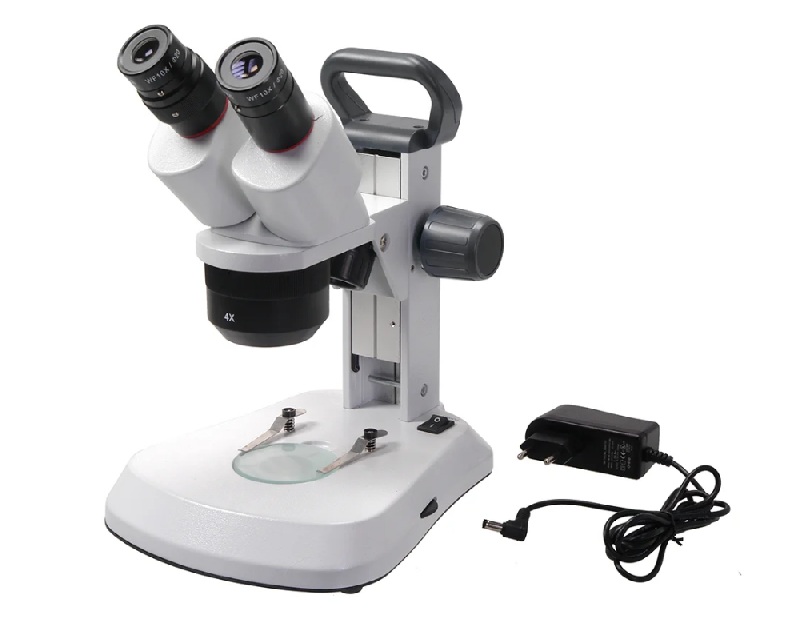
A device for conducting morphological analysis of preparations by the type of transmitted light can be used for observations.
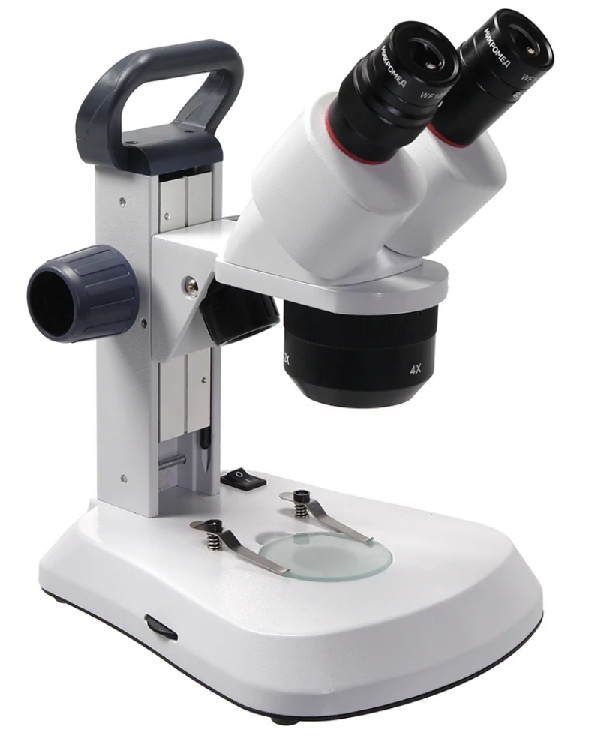

- using the bright field method;
- with high-precision assembly;
- changing the lens does not provoke the loss of the drug from the field of view;
- without additional focusing after changing lenses;
- the presence of an emphasis to protect the main lens;
- springy frames on lenses at 40x and 100x magnification;
- with built-in illuminator;
- the presence of a two-coordinate table;
- with LED brightness control;
- convenient compact form;
- light, weight 3.5 kg;
- suitable for medical work and biological laboratories;
- recommended for diagnostics in medical institutions and veterinary clinics;
- to study sections, smears of biological material in a stained and unstained state;
- compatible with a video eyepiece due to the design of the nozzle;
- used in universities for training;
- low inertia of the LED;
- with coaxial focusing handles, table;
- without the need for high voltage for the LED;
- the possibility of purchasing in the online store.
- not found.
Levenhuk 850B
votes 1

The microscope for professional biologists allows working on the principle of dark and bright fields.

- has an inclination angle of 30°;
- conversion of the condenser to the Abbe type by lifting up;
- fields are changed by turning the ring;
- with 4 lenses;
- optics with full multilayer coating;
- equipped with three filters, immersion oil;
- the presence of a swivel nozzle;
- with coarse and fine focusing;
- with diopter adjustment;
- interpupillary distance adjustable from 55 to 75 mm;
- object table 155x140 mm;
- with mains supply;
- the ability to install a digital camera;
- with built-in dark field condenser.
- missing.
LOMO Mikmed 5
votes 0
For more than 100 years, the well-known enterprise of St. Petersburg has been producing optical devices, constantly introducing new technologies, and holding the highest brand of products.
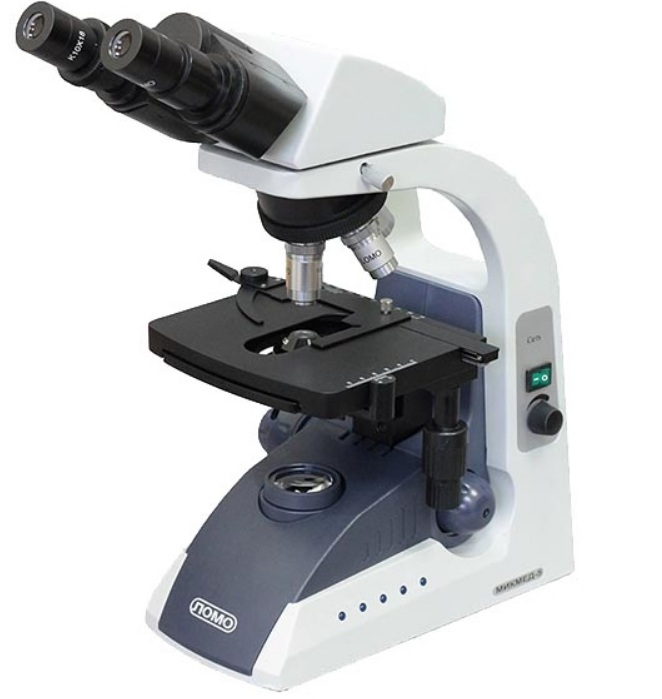
- biological class of optics;
- suitable for laboratory equipment;
- high-precision and coarse focusing;
- with a tilt angle of 30°;
- by type of light field;
- the presence of diopter adjustment;
- with a change in interpupillary distance in the range of 55-75 mm;
- with a possible change in the brightness of the backlight;
- subject area 155*140 mm;
- metal case;
- works from the network;
- light weight 7 kg.
- no.
Models of the "New" class
BIOMAT SZM-45N-V
votes 0
The stereomicroscope for a wide range of applications is recommended for work in biology, electronics manufacturing, the metallographic sector and mechanical engineering.
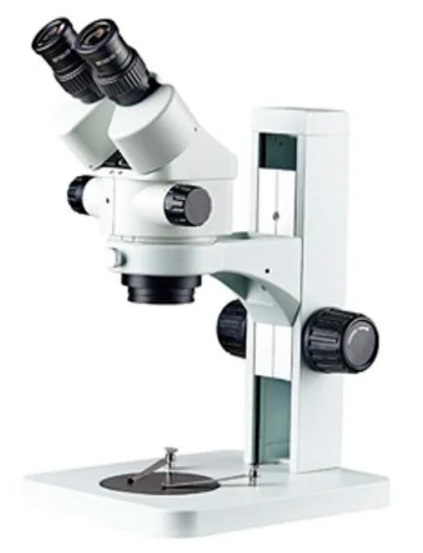
- suitable for laboratory observations;
- the presence of additional eyepieces;
- nozzle with an angle of inclination of 45 ° has a lock and the ability to turn up to 360 °;
- with interpupillary distance from 54 to 76 mm;
- diopter setting;
- stereo zoom eyepieces 6.4˸1;
- with a working focus range of 50 mm;
- the presence of a LED illuminator LED;
- purchase in the online store.
- not found.
Armed XS-90
votes 0
The optics of the famous Russian brand is changing along with innovative technologies and tirelessly maintains a high level of quality.
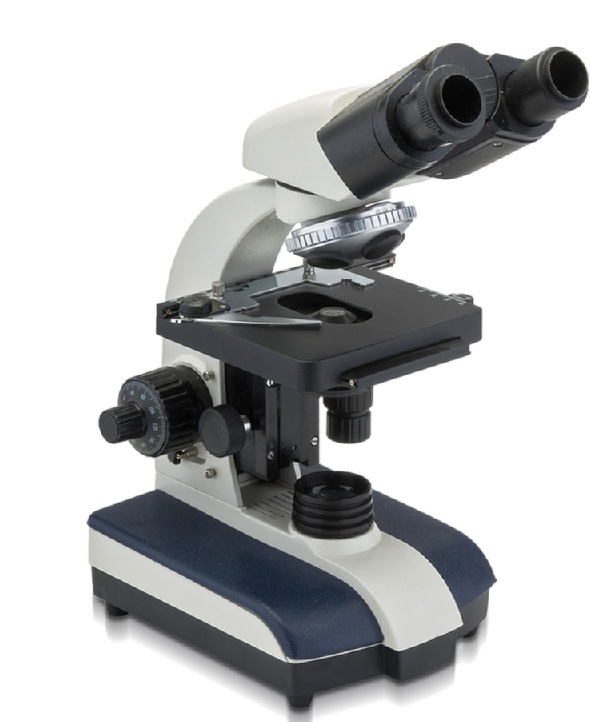
- the presence of a swivel nozzle;
- with iris diaphragm;
- convenient object table 130*125 mm;
- with diopter adjustment;
- all-metal reliable case;
- with a scaling factor of 6.5˸1;
- tube 160 mm long;
- the presence of brightness control;
- movement of the subject area along the coordinate axes 30x70 mm;
- with 4 lenses;
- light weight of 4.1 kg;
- convenient and compact;
- available in online sales;
- long warranty period.
- missing.

| The best binocular microscopes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Binoculars from a foreign manufacturer | |||||
| Model | Increase | Lenses, quantity, pcs. | Eyepieces, fold | Numerical aperture condenser | Light, source | |
| BRESSER 57-22100 Researcher Bino | 40÷1000 | 4 | 10 | Abbe, iris diaphragm | LED 20 W | |
| Celestron LABS CB2000CF 44231 | 40÷2000 | 4 | WF10x; WF20x | −”− | halogen | |
| Crystallite ST-60-L | 20÷40 | 2 | WF10x | - | LED, ring type | |
| Eschenbach 10-20x | 10-20x | 2 | - | - | LED, ring type, T 5800 K | |
| Saike Digital SK2126S | 7-45 times | 2 | WF10x; WF20x | −”− | ||
| 2. | Devices from a domestic manufacturer | |||||
| Micromed MS-1 var.1C | 60÷640 (option 2000) | 3 | 10/18, 16/15 | Abbe, 1.25 | LED with T 4600 K; 5 V; 0.5W | |
| Levenhuk 850B | 40÷2000 | 4 | Plan WF10x; Plan WF20x | - | halogen | |
| BIOMAT SZM-45N-V | 7-45 times | 0.7x -4.5x, stereo zoom; 6.4˸1 | WF 10x/20 mm | - | LED 5V;3 W, transmitted, reflected | |
| Armed XS-90 | 4-100x | 4 | WF 10x; WF16x | iris diaphragm | - | |
| LOMO Mikmed 5 | 40-1500x | 4 | 10x/18 15x/11 | −”− | LED |
Conclusion
Innovative technologies have made it possible to expand the range of optics, in particular, microscopes. Depending on the importance of the parameters required in research and observation, it is important to make the right choice of binocular that will meet the expectations of the researcher.
new entries
Categories
Useful
Popular Articles
-

Top ranking of the best and cheapest scooters up to 50cc in 2022
Views: 131651 -

Rating of the best soundproofing materials for an apartment in 2022
Views: 127690 -

Rating of cheap analogues of expensive medicines for flu and colds for 2022
Views: 124519 -

The best men's sneakers in 2022
Views: 124033 -

The Best Complex Vitamins in 2022
Views: 121940 -

Top ranking of the best smartwatches 2022 - price-quality ratio
Views: 114980 -

The best paint for gray hair - top rating 2022
Views: 113395 -

Ranking of the best wood paints for interior work in 2022
Views: 110318 -

Rating of the best spinning reels in 2022
Views: 105329 -

Ranking of the best sex dolls for men for 2022
Views: 104366 -

Ranking of the best action cameras from China in 2022
Views: 102216 -

The most effective calcium preparations for adults and children in 2022
Views: 102011









